Pros And Cons Of Nonfasting Versus Fasting Lipid Profiles
Because fasting has previously been the standard before blood sampling for a lipid profile in most countries, the shift toward using nonfasting rather than fasting lipid profiles naturally has been debated over the last few years : many arguments and novel data for and against have been presented from the perspective of the patient, laboratory, and clinician.
With the current evidence base, it could be argued that the use of nonfasting lipid profiles is evidence-driven, whereas continued use of fasting lipid profiles is largely belief-driven . Indeed, a main argument for keeping fasting lipid profiles is that We have always done it that way! when today, prospective evidence from more than 300,000 individuals is available suggesting that nonfasting lipid profiles are as good as, if not better than, fasting lipid profiles in predicting future cardiovascular events .
Central Illustration.
Comparison of Fasting and Nonfasting Lipid Profiles
Direct comparison of arguments for and against use of random, nonfasting, and fasting blood sampling. Nonfasting blood sampling can occur anytime during the 24-h cycle, irrespective of what and when the individual ate before blood sampling. By contrast, a fasting blood sample can only be drawn after a period without food intake for 8 or more hours, which often means that a natural small fast of a few hours in the early morning will be extended, possibly until noon, before the blood is drawn.
Lipid Panel: Fasting Vs Non
- Post published:
- Post category:Blog
Practitioners have long prescribed a fast of 8-12 hours before a lipid panel, also known as a cholesterol test. Indeed, most doctors who have practiced for over 10-15 years will still require fasting to prevent the results of the test from being affected by the patients metabolic processes. However, more recent research suggests that lipid panel fasting vs non-fasting results are more complexly indicated depending on the situation.
Continue reading to learn about fasting vs non-fasting results for lipid panel testing. Remember to follow your doctors orders and ask them about any changes you make to your routine.
Risk Factors And Complications
High blood triglycerides can be a risk factor for heart disease. Its unclear whether triglycerides can cause the buildup of plaque in your arteries thats associated with many types of heart disease. At extreme levels of 1,000 mg/dL or more, blood triglycerides can cause acute pancreatitis.
Elevated triglyceride levels can be a sign of metabolic syndrome. Metabolic syndrome is a collection of conditions that include:
- an excessively large waistline, which is defined as greater than 35 inches in women or 40 inches in men
- elevated blood pressure
- low HDL, or good cholesterol
- elevated triglycerides
Each one of these conditions carries risks and complications of its own, and all can be linked to the development of heart disease. Type 2 diabetes, which is characterized by high blood sugar and resistance to the hormone insulin, is also often associated with elevated triglycerides. Other causes of elevated triglyceride levels are:
- hypothyroidism, which is caused by a deficient thyroid gland
Recommended Reading: When Is Ramadan Fasting Over
Evidence Supporting Nonfasting Lipid Testing
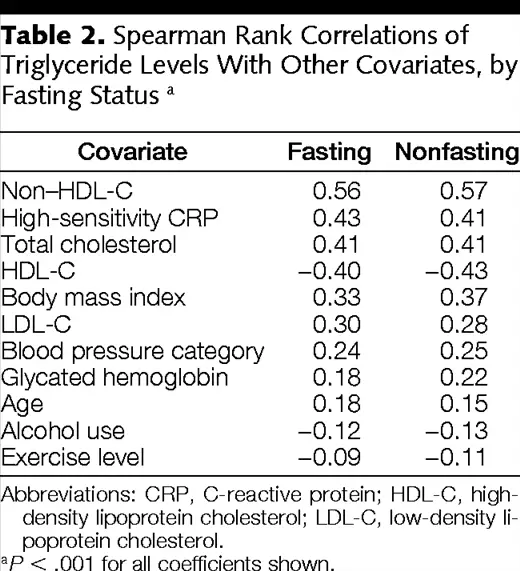
The adequacy of nonfasting lipid testing for general screening for cardiovascular disease has been verified in large prospective studies over the past several decades.,, These studies evaluated cardiovascular event and mortality rates and found consistent associations of nonfasting lipid levels with cardiovascular disease. Studies that included both fasting and nonfasting patient populations found similar or occasionally even greater cardiovascular risk associations for nonfasting lipid measurements compared with fasting lipid measurements.
The Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration reviewed the data from 68 studies in more than 300,000 people and found that the relationship between lipid levels and incident cardiovascular events was just as strong when nonfasting lipid values were used. In fact, at least 3 large statin trials reviewed used nonfasting lipids.
Genetic studies using mendelian randomization have also linked nonfasting triglyceride levels to an increased risk of cardiovascular events and of death from any cause.,
Therefore, the evidence overall suggests that nonfasting lipid measurements are acceptable with respect to risk assessment, and indeed may be preferred in most instances, especially in patients with an atherogenic metabolic milieu that may otherwise be masked by the fasting state.
Implications For Clinical Trials
Nonfasting, compared with fasting lipid profiles will also help recruit and retain patients in lipid-lowering trials, and likely will reduce trial costs. This is because ethical committees in many countries do not allow patients to be asked to fast before the first study visit, which means an extra study visit simply for the lipid profile. Also, the use of nonfasting lipid profiles during follow-up visits will be more practical for study participants, and will allow study visits at any time of the day, whatever suits the individual study participant. Finally, because nonfasting lipid profile measurements are used more and more commonly in clinical practice, it is equally important that future lipid-lowering trials are conducted under nonfasting conditions to match the clinical reality of the future.
Also Check: Which Intermittent Fasting Is The Best
What To Expect During A Test For Triglycerides
Your doctor can measure your triglyceride levels using a simple blood draw. The process is the same if the test is measuring your fasting or nonfasting triglyceride levels. If your doctor wants to measure your fasting triglyceride levels, they will likely instruct you to fast for a given amount of time. They may also ask you to avoid certain medications.
If the test is measuring nonfasting triglycerides, there are typically no dietary restrictions. However, your doctor may request that you avoid eating a meal thats unusually high in fat prior to the test.
If you have a history of fainting during blood draws, notify the lab technician who will be collecting your sample.
Nonfasting Lipid Testing: The New Standard For Cardiovascular Risk Assessment
-
Large population studies have shown that total cholesterol and high-densitylipoprotein cholesterol do not vary and low-densitylipoprotein cholesterol and triglycerides vary slightly after eating.
-
Use of non-HDL cholesterol in a nonfasting plasma sample captures the atherogenic effect of remnant lipoproteins and is a better indicator of cardiovascular risk than LDL cholesterol.
-
Nonfasting testing for baseline and follow-up complete lipid profiles, including LDL cholesterol and triglycerides, is recommended by the Canadian Cardiovascular Society and the College of Family Physicians of Canada guidelines for lipids.
-
Removing the need to have the patient fast for testing of lipid profiles increases the convenience, safety, and timeliness of screening and follow-up testing, is appreciated by patients and may entirely remove the need for fasting prior to testing.
The modified laboratory requisition for lipid testing in British Columbia will, as of January 2019, indicate that fasting is not required for any full or partial lipid profile unless requested by the physician . An audit of the laboratory information system used by the Vancouver Coastal Health region showed that 15% of outpatient lipid profiles were performed in patients who had not fasted greater than 10 hours and that no lipid tests were cancelled because of nonfasting , suggesting partial concordance with the new guidelines.
Don’t Miss: How Does Intermittent Fasting Work 16 8
Risks And Complications Of High Or Low Triglyceride Levels
The relationship between triglycerides and cardiovascular disease is not fully understood, but there is growing evidence that high levels of triglycerides in the blood increases the risk of heart problems.
Triglycerides interact with the body in complex ways, and scientists continue to study these interactions. Many studies have shown triglycerides add to inflammation that can increase damage and blockages to blood vessels.
High triglyceride levels can also lead to an inflamed pancreas or pancreatitis, which is a serious medical condition. Pancreatitis can cause severe abdominal pain, which can extend from the upper stomach to the back and can even lead to life-threatening organ failure.
- metabolic syndrome
Some medications can also have the same effect on blood triglyceride levels
In all these cases, doctors will work with the individual to treat the underlying condition or make changes to their medications.
A person can make specific lifestyle choices to reduce their triglyceride levels, including:
- avoiding smoking
- getting plenty of regular exercise
- reducing alcohol intake
- eating a healthful diet
If TG and cholesterol test results and other health markers suggest someone is at high risk of heart disease, a doctor will likely recommend treatment and a follow-up plan.
Most crucial of all is undergoing lifestyle changes, such as adopting a healthful diet, daily physical activity, and quitting smoking.
Lipid Panels: Fasting Or Non
Traditionally, lipid panels are drawn under fasting conditions. Is there data supporting decreased accuracy in a non-fasting lipid panel?
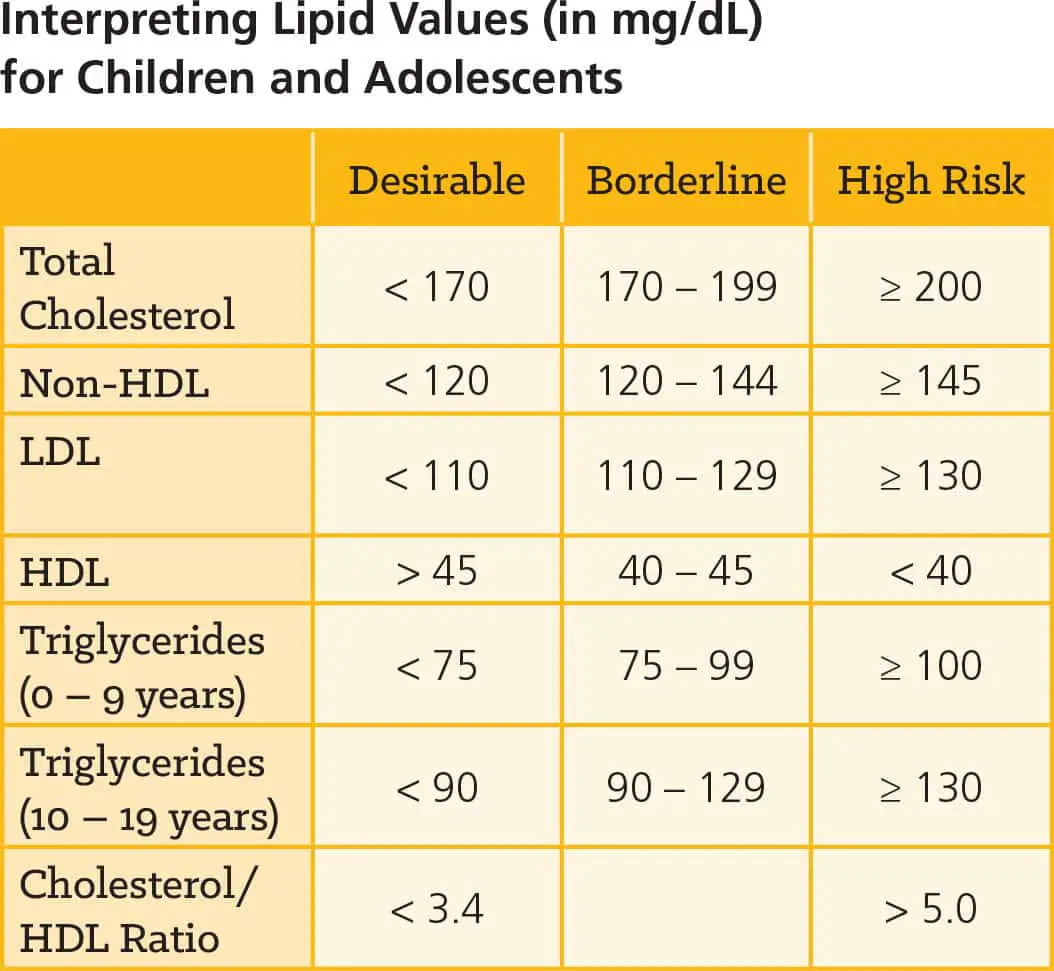
Cholesterol is an essential tool for our body for the synthesis of hormones, vitamin D, and bile acids. However, an excess of cholesterol pose a serious threat to our health as it contributes to heart disease, stroke, and other comorbidities. Knowing our cholesterol level is fundamental in helping us identify when and how to take proper measures towards keeping our cholesterol levels within normal ranges. To take precautions and preventative measures at the right time, most doctors mandate a lipid panel at least once every year for males 35 years of age, and for females 45 years of age. A lipid panel is a blood test that measures the following lipidscholesterol, triglycerides, high-density lipoprotein , and low-density lipoprotein .
Recently, various large prospective cohort studies and a meta-analysis have been published, investigating the possibility of a relationship between fasting and nonfasting serum triglycerides with cardiovascular disease. The studies demonstrated that fasting triglycerides augment the adjusted hazard ratios for cardiovascular disease risk 1.7 times as much , and nonfasting levels about 2.0 times as much .
Don’t Miss: How Fast Can You Lose Weight By Intermittent Fasting
Types Of Cholesterol Tests
It is not necessary to fast before a total cholesterol test because the value does not change significantly after eating, according to the Harvard Health Publications 2. A lipid profile, which includes values for total cholesterol, as well as individual values for LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol and triglycerides, another lipid in the blood, requires you to fast.include:
- A lipid profile
- another lipid in the blood
- requires you to fast
Why Do I Need A Lipid Panel Blood Test
There are several reasons why you may need a lipid panel blood test. Healthcare providers use lipid panels often for screen and monitoring purposes.
If you have one or more risk factors for cardiovascular disease, your provider may suggest frequent screening through the use of a lipid panel to try to catch elevated cholesterol levels before you have symptoms. Risk factors for cardiovascular disease include:
- Being over age 45 if youre a man or you were assigned male at birth and over 50 if youre a women or you were assigned female at birth.
- Having a high cholesterol result on a previous test.
- Having diabetes or prediabetes.
- Having a first-degree relative, such as a parent or sibling, who developed heart disease at an early age .
Children can also have high cholesterol, so your child may need a lipid panel blood test. Cholesterol levels in children are linked to three factors: heredity, diet and obesity. In most cases, kids with high cholesterol have a parent who also has elevated cholesterol.
While providers mostly use lipid panels for screening or monitoring cholesterol levels, providers sometimes use them as part of the diagnostic process for certain health conditions that can affect your lipid levels, including:
If youre experiencing symptoms of any of these conditions, your provider may have you undergo a lipid panel blood test.
Recommended Reading: Why Is Intermittent Fasting Effective
The History Behind Fasting Cholesterol Tests
When doctors test for cholesterol, we almost always order a group of tests called a lipid panel . This panel typically includes four separate measures:
- Total cholesterol concentration.
- Low-density lipoprotein* cholesterol, often called the bad cholesterol. The amount of LDL in your blood strongly predicts your risk of cardiovascular disease, as higher levels are associated with development of plaque in the arteries.
- High-density lipoprotein cholesterol, often called good cholesterol because higher levels protect against heart disease.
- Triglycerides . High levels of triglycerides are also associated with vascular disease, although this relationship isnt as well defined.
*Lipoproteins are the packages that transport cholesterol in the bloodstream.
Lipids have traditionally been drawn after a fast for two main reasons. The first was to minimize variation, since eating can affect some lipid levels. The second was to produce a better calculation of LDL-cholesterol, which is often derived from an equation thought to provide highly distorted results after eating. However, more recent studies have largely negated these concerns.
Is It Time To Abandon Fasting For Routine Lipid Testing
Yes. The time has come to change the way we think about fasting before routine lipid testing. We now have robust evidence supporting the routine use of nonfasting lipid testing. Fasting lipid testing is rarely needed, but may be considered for patients with very high triglycerides or before starting treatment in patients with genetic lipid disorders. For most patients, nonfasting lipid testing is appropriate: it is evidence-based, safe, valid, and convenient. More widespread adoption of this strategy by US healthcare providers would improve quality of care and patient and clinician satisfaction.
Also Check: What Counts As Intermittent Fasting
Farewell To The Fasting Cholesterol Test
- By Naomi D. L. Fisher, MD, Contributor
ARCHIVED CONTENT: As a service to our readers, Harvard Health Publishing provides access to our library of archived content. Please note the date each article was posted or last reviewed. No content on this site, regardless of date, should ever be used as a substitute for direct medical advice from your doctor or other qualified clinician.
At a recent meeting I offered a visitor lunch which she declined with obvious regret. She was hungry, and it was noon. But she was headed to her annual physical, and eating beforehand would mean returning another morning for a fasting cholesterol level. Most of us can relate to her annoyance, but thankfully this may soon be a thing of the past.
Doctors have traditionally ordered cholesterol tests to be drawn after an overnight fast. But this requirement causes a significant burden on both sides of the health care equation. Most people hate to fast. Skipping meals is particularly difficult for active people, people with diabetes, and children. Yet coming back for another visit is even more of a hassle, so many people just dont bother. And it has been a drain for doctors, too, resulting in repeat test orders, phone calls, and patient visits.
Historical Development Of Nonfasting Lipid Profiles
The Danish Society for Clinical Chemistry recommended nationwide use of nonfasting lipid profiles in 2009 , followed by similar endorsement in 2011 by the American Heart Association and, in 2014, by the U.K. National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guidelines and guidelines from Veterans Affairs and U.S. Department of Defense . This was followed by similar recommendations in 2016 by the European Atherosclerosis Society and European Federation of Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine, in a joint consensus statement with detailed discussion of the evidence, as well as the clinical implications of using nonfasting, rather than fasting lipid profiles . Later in 2016, this was followed by a similar endorsement for nonfasting lipid profiles by the Canadian Hypertension Education Program guidelines , the Canadian Cardiovascular Society guidelines , the European Society of Cardiology and the European Atherosclerosis Society guidelines for the management of dyslipidemias , and by consensus of 5 medical societies in Brazil . Finally, in 2017, endorsement of the use of nonfasting lipid profiles came from the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and the American College of Endocrinology .
Read Also: When Should I Eat Intermittent Fasting
What Is A Lipid Panel Used For
Healthcare providers use lipid panels to help assess someones cardiovascular health by analyzing cholesterol in their blood and to help diagnose other health conditions.
Reasons a provider may order a lipid panel include:
- As a routine test to determine if your cholesterol level is normal or falls into a borderline-, intermediate- or high-risk category.
- To monitor your cholesterol level if you had abnormal results on a previous test or if you have other risk factors for heart disease.
- To monitor your bodys response to treatment, such as cholesterol medications or lifestyle changes.
- To help diagnose other medical conditions, such as liver disease.
What Should I Expect During My Lipid Panel Blood Test
You can expect to experience the following during a blood test, or blood draw:
- Youll sit in a chair, and a healthcare provider will check your arms for an easily accessible vein. This is usually in the inner part of your arm on the other side of your elbow.
- Once theyve located a vein, theyll clean and disinfect the area.
- Theyll then insert a small needle into your vein to take a blood sample. This may feel like a small pinch.
- After they insert the needle, a small amount of blood will collect in a test tube.
- Once they have enough blood to test, theyll remove the needle and hold a cotton ball or gauze on the site to stop the bleeding.
- Theyll place a bandage over the site, and youll be finished.
The entire procedure usually takes less than five minutes.
Read Also: For Thyroid Test Is Fasting Needed
When Should I Call My Doctor
If you develop new risk factors for cardiovascular disease, contact your healthcare provider. They may have you undergo a lipid panel or more frequent lipid panel screening.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Seeing an abnormal test result can be stressful. Know that having an abnormal lipid panel result doesnt necessarily mean you need treatment. While cholesterol and triglyceride levels can play a significant role in your overall health, many other factors contribute to your risk for cardiovascular disease. Your healthcare provider will take many factors about your health and history into consideration when determining the next steps. Together you will decide on a plan that works best for you.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 11/09/2021.
References