Diagnosing Prediabetes Type 2 And Type 1 Diabetes
Depending on which country or medical organization you ask, the qualifying numbers for normal versus prediabetes versus diagnosed type 1 or type 2 diabetes can vary slightly. The following blood sugar and A1c the general results are used to diagnosed prediabetes and diabetes according to sources including the American Diabetes Association and Diabetes UK:
Prediabetes
- HbA1c: 5.7 to 6.4 percent
- Fasting: 100 to 125 mg/dL
- 2 hours after a meal: 140 mg/dL to 199 mg/dL
Type 1 or 2 diabetes
- HbA1c: 6.5 percent or higher
- Fasting: 126 mg/dL or higher
- 2 hours after a meal: 200 mg/dL or higher
Please note: Type 1 diabetes tends to develop very quickly which means that by the time symptoms are felt, blood sugar levels are generally well above 200 mg/dL all the time. For many, symptoms come on so quickly they are dismissed as the lingering flu or another seemingly ordinary virus.
By the time blood sugar levels are tested, many newly diagnosed type 1 patients will see levels above 400 mg/dL or higher. If you do suspect that you or a loved-one has type 1 diabetes, visit your primary care or urgent care immediately and ask for a urine test to measure ketones in addition to testing blood sugar levels and A1c.
Read more about ketones at diagnosis in Diabetes StrongsDiabetic Ketoacidosis Guide.
Dont Miss: Did Intermittent Fasting Work For You
Chart For Normal Fasting Blood Sugar Levels
| TAKE-HOME TIPS |
Normal fasting blood sugar levels are considered fasting blood sugar levels between 80 mg/dl and 100 mg/dl. However, nowadays, this normal range is changed due to different reference ranges of laboratories use.
These figures come out when you measure your blood sugar level in the morning after have been fasting for at least 8 hours.
This is the time between the dinner and your breakfast. Everything you eat influence in you fasting blood sugar level.
What you need to do is to keep your fasting blood sugar levels at a normal range, I.e as lowest as possible. If you find it so difficult for you, let our specialized medical team do the job.
Dont Miss: Is Intermittent Fasting Good For Endomorphs
What Are Common Complications From Living With Diabetes
Cardiovascular Disease
- Over time, diabetes can damage arteries, which may result in high blood pressure.
- If not controlled, this can lead to stroke, heart failure or heart attack.
- People with diabetes need to keep their blood pressure and cholesterol under control.
Kidney Disease
- Kidney damage can develop in some people with diabetes.
- If left untreated, this can lead to more severe kidney damage or kidney failure.
- If you have diabetes, you should have your kidney function tested regularly.
Did You Know?
A healthcare provider can help with monitoring blood glucose levels, as well as ensuring that necessary preventive care treatments and advice are received in a timely manner.
Vision Loss
- Diabetic eye disease can lead to loss of vision and blindness.
- Regular eye exams can help find problems that can be treated if found early.
Lower Limb Amputation
- Over time, diabetes can damage sensory nerves, especially in the hands and feet.
- As a result, people with diabetes may not feel a foot injury, such as a blister or cut. Even a small injury, if left untreated, can quickly become infected. This can lead to serious complications such as amputation.
- People with diabetes should regularly check their feet and skin for ulcers and wounds .
Other Complications
People with diabetes are likely to develop other conditions such as dental disease and mental illness .
Read Also: When To Workout During Intermittent Fasting
Diabetes Blood Sugar Level Goals
Upon waking before breakfast
- 70-130 mg/dl
- 4-7.2 mmol/l
Two hours after meals
- Under 180 mg/dl
- Under 10 mmol/l
Bedtime
- 90-150 mg/dl
- 5-8.3 mmol/l
The above levels, for people diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, are the general goals set by the American Diabetes Association and the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists.
As suggested earlier, there is some variation in the blood sugar levels goals set by different organizations. And additionally, your physician or healthcare team may set your goals at a more stringent level.
For instance, fasting levels:
- Between 70-100 mg/dL or 4-5.6 mmol/l
- 70-110 mg/dL or 4-6 mmol/l
- 70-130 mg/dL or 4-7.2 mmol/l
Once you have a type 2 diabetes diagnosis, the overall goals you should aim for is to get your blood sugar levels as close to normaloptimal levels as you possibly can.
BUT, as suggested above, often goals are set with higher targets initially. For instance, if you have a high reading of 250 or 300 , your physician or health practitioner may recommend 200 be an initial goal, then 180 , before gradually working toward 140 and lower.
The reason this is often recommended is you can experience symptoms of hypoglycemia if you bring your levels down very quickly. So working toward tighter and tighter control does take some time.
You should work with your healthcare team on this. But overall the most optimal targets to work toward are a fasting glucose under 100 mg/dl or 6 mmol/l. And an after-meal reading below 140 or 7.8.
What A1c Goal Should I Have
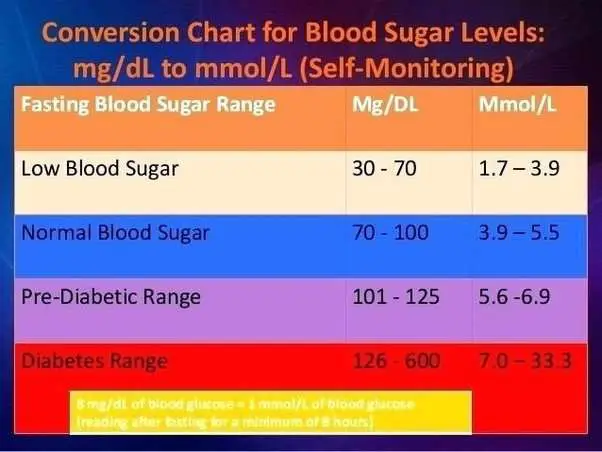
People will have different A1C targets, depending on their diabetes history and their general health. You should discuss your A1C target with your health care professional. Studies have shown that some people with diabetes can reduce the risk of diabetes complications by keeping A1C levels below 7 percent.
Managing blood glucose early in the course of diabetes may provide benefits for many years to come. However, an A1C level that is safe for one person may not be safe for another. For example, keeping an A1C level below 7 percent may not be safe if it leads to problems with hypoglycemia, also called low blood glucose.
Less strict blood glucose control, or an A1C between 7 and 8 percentor even higher in some circumstancesmay be appropriate in people who have
- limited life expectancy
Don’t Miss: How To Do Diet Fasting
Can Other Blood Glucose Tests Be Used To Diagnose Type 2 Diabetes And Prediabetes
Yes. Health care professionals also use the fasting plasma glucose test and the OGTT to diagnose type 2 diabetes and prediabetes. For these blood glucose tests used to diagnose diabetes, you must fast at least 8 hours before you have your blood drawn. If you have symptoms of diabetes, your doctor may use the random plasma glucose test, which doesnt require fasting. In some cases, health care professionals use the A1C test to help confirm the results of another blood glucose test.
Why Elevated Glucose May Lead To Weight Gain
Foods high in sugar and refined carbs may promote weight gain because of their impact on blood sugar and insulin levels. These foods are considered high-glycemic carbs because they are quickly digested and lead to rapid rises in blood sugar.
Examples of high-glycemic foods include:
- White bread, bagels, white rice, white-flour pasta
- Muffins, croissants, doughnuts, flavored instant oatmeal, most cereals
- Cakes, candy, cookies, and most desserts
- Corn and white potatoes
< p class=”pro-tip”> < strong> Learn more about < /strong> < a href=”/blog/foods-to-avoid-for-weight-loss”> 8 foods to avoid for weight loss< /a> < /p>
Occasionally eating some cake at a birthday party isn’t a big deal, but a diet high in these foods and low in other blood sugar balancing nutrients like fiber and protein can mean you have higher insulin levels than usual as your body tries to lower blood sugar. Over time, insulin can promote fat storage.
When your glucose spikes and you don’t burn the excess energy, your body converts the extra glucose to glycogen stored in your muscle tissue and liver or as fat stored in your adipose cells.
By learning how your blood sugar responds to food and exercise, you can keep your glucose in a target range that also promotes a healthy weight.
< p class=”pro-tip”> < strong> Learn more about < /strong> < a href=”/blog/ultra-processed-foods”> how ultra-processed foods affect blood sugar< /a> < /p>
You May Like: What Should Your Blood Sugar Be Fasting
Remedies For Low Sugar Levels
If you experience any low sugar symptoms, immediately test your blood glucose levels. For levels between 60 to 80 mg/dL, consume 15 grams of fast-acting carbs. Repeat the test after 15 minutes and eat till sugar levels settle to normal.
But if the levels are below 50 mg/dL and if the patient is conscious and able to eat, give 15 gm. of fast-acting carbs. But if the patient is unable to speak, dont give him anything to eat. Call emergency services immediately. If possible, administer glucagon via injection.
Chart showing levels of sugar i.e excellent, good, or action suggested
What Should A Non Fasting Blood Sugar Be
100% of these at the macrobiotic weight-reduction plan got right down to as a minimum below 110, whereas much less than 1/2 of these on the diabetes food regimen did.
So, higher consequences on fewer drugs.
They took diabetics and placed them on a 73% carbohydrate weight loss program, adding one hundred grams of carbs to their each day diet, and within the shape of grains.
This is not entire article. It continues …
- The Benefits Of Soup For The Human Body: Types Of Soups, Rec…
- Physiology Of Digestion: Stages, Organs, Enzymes
- Vitamins In Preparation For Pregnancy: Main Nutrients And Th…
- Useful Properties Of Spices And Spices: Application Table, C…
- Why Do You Always Want To Eat
- Safe Weight Loss Without Diets And Miracle Cures
- Sports Nutrition For Joints And Ligaments
- B6 Products: Vitamin Intake Norms
- Diet For Bowel Diseases: Menu, Allowed And Prohibited Foods
- Antioxidants In Food: The Most Faithful Defenders Of Our Bod…
Don’t Miss: What Is Do Fasting App
Different Levels And What They Mean
The ranges of safe levels of blood glucose depend on factors such as what time of day it is and when you last ate. Safe levels of blood sugar are high enough to supply your organs with the sugar they need, but low enough to prevent symptoms of hyperglycemia or complications of diabetes which follow the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases guides. Dangerous levels of blood glucose are outside of this range.
The target levels can also vary if you have diabetes. For example, if you are diabetic and are monitoring your blood sugar, you might get a reading of 65 mg/dl. That is considered to be mild hypoglycemia, and you would be wise to eat 15 grams of fast-acting carbohydrates and retest your blood sugar in 15 minutes.
If you were not diabetic, you probably would not know that your sugar was low because you would not test and because you would not symptoms, and you would not act.
That is fine because your body is capable, under normal circumstances, of raising your blood glucose to healthy levels when needed, even if you have not eaten. It is important to keep them in control to help prevent issues like heart disease or nerve damage.
Looking for the best prediabetes diet? Learn what foods are best to help you manage your prediabetes.
What Abnormal Results Mean
If you had a fasting blood glucose test:
- A level of 100 to 125 mg/dL means you have impaired fasting glucose, a type of prediabetes. This increases your risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- A level of 126 mg/dL or higher usually means you have diabetes.
If you had a random blood glucose test:
- A level of 200 mg/dL or higher often means you have diabetes.
- Your provider will order a fasting blood glucose, A1C test glucose tolerance test , depending on your random blood glucose test result.
- In someone who has diabetes, an abnormal result on the random blood glucose test may mean that the diabetes is not well controlled.
Other medical problems can also cause a higher-than-normal blood glucose level, including:
- Overactive thyroid gland
- Swelling and inflammation of the pancreas ( pancreatitis
- Stress due to trauma, stroke, heart attack, or surgery
- Rare tumors, including
- Weight loss after weight loss surgery
- Vigorous exercise
Some medicines can raise or lower your blood glucose level. Before having the test, tell your provider about all the medicines you are taking.
For some thin young women, a fasting blood sugar level below 70 mg/dL may be normal.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Most Effective Intermittent Fasting Schedule
What Is High Blood Sugar
If your blood sugar levels are chronically higher than normal, then this is referred to as hyperglycaemia. This is a common issue for those suffering from diabetes. The condition can also affect pregnant women who have gestational diabetes and occasionally those who are severely ill .
Some of the symptoms of hyperglycaemia include:
- Increased thirst
- Blurred vision
- Issues with concentration and/or thinking
If severe hyperglycaemia is left untreated the condition can lead to organ and tissue damage as the excess glucose present in the body can make it difficult for the organs and cells to function correctly. The disorder can also impair the immune system response in the healing of wounds and cuts.
Random Blood Sugar Test
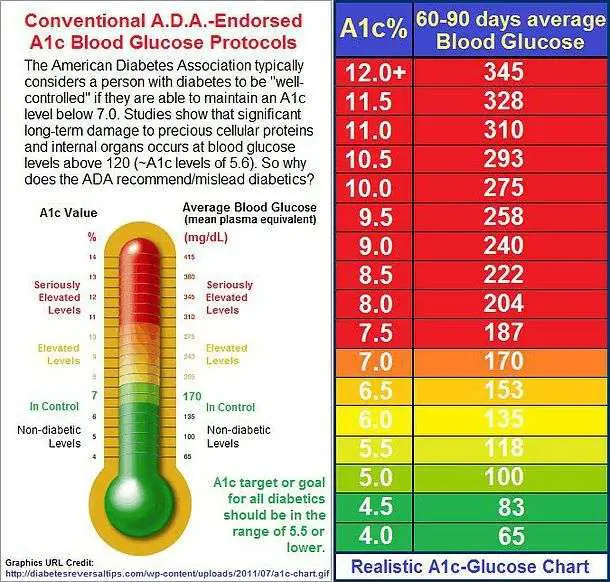
This measures your blood sugar at the time youre tested. You can take this test at any time and dont need to fast first. A blood sugar level of 200 mg/dL or higher indicates you have diabetes.
Random Blood Sugar Test| 140 mg/dL or below | N/A |
*Results for gestational diabetes can differ. Ask your health care provider what your results mean if youre being tested for gestational diabetes.Source: American Diabetes Association
If your doctor thinks you have type 1 diabetes, your blood may also tested for autoantibodies that are often present in type 1 diabetes but not in type 2 diabetes. You may have your urine tested for ketones , which also indicate type 1 diabetes instead of type 2 diabetes.
Read Also: What Is Best Intermittent Fasting For Weight Loss
Normal Blood Sugar Levels Chart For Adults
Glucose level determination in the blood is essential for people with suspected diabetes or diabetics and for completely healthy people. Normal blood sugar levels have been established by specialists based on many years of thorough research and clinical observations.
Contents
They allow the diagnosis of metabolic diseases and facilitate the application of appropriate therapy. Early detection of changes in the body and proper treatment and prevention is the key to success.
Sugar plays a vital role in the body. It is one of the primary sources of energy for the body belongs to the group of carbohydrates, which in the process of digestion are broken down into simple sugars
- glucose
- Fructose
Blood glucose level should be more or less at the same level, but if it starts to decrease or exceed the level, your body will stop functioning correctly, which results in various disorders. Insulin, a hormone secreted by the pancreas, maintains sugar levels.
The presence of sugar in the blood is so necessary that without it, our bodies may stop functioning correctly, the nervous system, the skeletal and muscular systems, the lymphatic system, and your organs.
Blood sugar testing is used primarily to diagnose diabetes, but healthy people should also monitor blood glucose levels.
Remedies For High Sugar Level
If the blood sugar level is between 180 to250 mg/dL, seek medical advice and take medicines. Cut off a fast-acting carb diet. Dont take processed food and sugary items.
If the blood sugar level is> 250 mg/dL, you need immediate medical attention. If left untreated, it can lead to coma and high ketones in the blood. So test for ketones and get insulin therapy as soon as possible.
If you experience high sugar levels on regular basis, you are advised to do the following:
Many diabetic patients are aware of the changes they need to make in their diet or daily routine but are not able to follow them due to various reasons. Lack of motivation and proper knowledge is the most common reasons. A constant push from a diabetes reversal coach along with the guidance of a Diabetologist can help regulate blood sugar levels.
Also Read:HbA1c Levels
Read Also: How Does Fasting Make You Lose Weight
What Affects Blood Glucose Levels
Before we get into normal blood sugar levels for people without diabetes, and for people with diabetes, letâs explore the factors that affect blood glucose levels:
This is not even nearly an exhaustive list – you can find a fuller list of factors that affect blood glucose here – but these are some of the most common reasons for blood glucose fluctuations. There are plenty of biological factors that affect blood sugar as well, like puberty, menstruation, and having Celiac disease.
Itâs also easy to overlook behavioural and decision-making factors that have a way bigger effect on our blood glucose levels than we actually think. In reality, the number of times you check your blood glucose, your decision-making biases and social pressures influences your attitude towards controlling your blood sugar levels, so often has a significant effect.
This really illustrates the strength of Time-in-Range, which is considered the gold standard in blood glucose monitoring. Instead of focusing on an average, like A1C, or one measurement, like fasting glucose, Time-in-Range accounts for all the variations in your blood sugar levels, giving you a percentage of time you are within your target glucose range.
See more about our Time-in-Range in this blog post.
Cgm Studies In Nondiabetic Individuals
One study from 2009 entitled Reference Values for Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Chinese Subjects looked at the glucose levels of 434 healthy adults using CGM and found the following:
- On average, their daily glucose levels stayed between 70140 mg/dl for 93% of the day, with very small portions of the day spent above 140 mg/dl or below 70 mg/dl.
- Also, their mean 24-hour glucose levels were around 104 mg/dl
- 1-hour post-meal glucose values average 121-123 mg/dl for breakfast, lunch, and dinner
- 3-hour post-meal glucose values were around 97-114 mg/dl.
- Peak post-meal values appeared to be around 60 minutes after eating.
- Mean fasting glucose was 86 ± 7 mg/dl.
- Mean daytime glucose was 106 ± 11 mg/dl.
- Mean nighttime glucose was 99 ± 11 mg/dl.
A 2010 study, Variation of Interstitial Glucose Measurements Assessed by Continuous Glucose Monitors in Healthy, Nondiabetic Individuals, looked at a healthy population of 74 individuals that included children, adolescents, and adults during daily living using CGM. This research showed that:
- Glucose levels stayed between 71-120 mg/dl for 91% of the day.
- Levels were lower than 70 mg/dl for 1.7% of the time and greater than 140 mg/dl, only 0.4% of the time.
- Mean 24-hour glucose was 98 ± 10 mg/dl.
- Mean fasting glucose of 86 ± 8 mg/dl.
Compared to the first study mentioned, these healthy, nondiabetic individuals appeared to have a tighter range of glucose, spending the vast majority of the 24-hour period between 71-120 mg/dl.
Recommended Reading: What Is Water Fasting In Keto