Fasting & Elevated Blood Glucose
Type 2 diabetes for 20+ years. Started keto with intermittent fasting in January 2019. Why would my fasting blood glucose numbers during my 18-24-hour fast be elevated, then come down to normal ranges after eating?
Mindy
Fasting can definitely raise blood glucose. This is due to the effect of insulin falling and the rising counter-regulatory hormones including increased sympathetic tone, noradrenaline, cortisol and growth hormone, in addition to glucagon. These all have the effect of pushing glucose from liver storage into the blood. This is normal. If you are not eating, you want to use some stored glucose. The question is this if you are not eating, and your blood glucose went up, where did that glucose come from? It can only have come from your own body . So, its a natural phenomenon, and the fasting now allows your body to use some of the glucose for energy.
Dr. Jason Fung
Diabetes Tracking And Treatment
- Follow your diabetes treatment plan: Understand the treatment plan before leaving the healthcare providers office and discuss barriers that could prevent you from following the program. Attend all follow-up visits.
- Consistently take prescribed medications: If a healthcare provider has prescribed medications to reduce blood sugar levels, take them regularly. Some people only take medication when they arent feeling well, but these medications dont work unless taken consistently.
- Monitor and track blood sugar: Regular blood sugar monitoring is the most important step in diabetes management, according to the CDC. Healthcare providers can inform patients of different types of meters and help patients find the best one for them. Providers can also tell patients how often to check their blood sugar and what their target blood sugar range is.Keep a log of your blood sugar levels to look for patterns and triggers for blood sugar spikes and lows. If you wear a continuous glucose monitor, you can use the data. Learning what causes blood sugar to rise or decrease can help you create a plan to keep it consistent.
Glucose Screening Tests During Pregnancy
TWO-STEP TESTING During the first step, you will have a glucose screening test: You DO NOT need to prepare or change your diet in any way. You will be asked to drink a liquid that contains glucose. Your blood will be drawn 1 hour after you drink the glucose solution to check your blood glucose level. If your blood glucose from the first step is too high, you will need to come back for a 3-hour glucose tolerance test. For this test: DO NOT eat or drink anything for 8 to 14 hours before your test. You will be asked to drink a liquid that contains glucose, 100 grams . You will have blood drawn before you drink the liquid, and again 3 more times every 60 minutes after you drink it. Each time, your blood glucose level will be checked. Allow at least 3 hours for this test. ONE-STEP TESTING You need to go to the lab one time for a 2-hour glucose tolerance test. For this test: DO NOT eat or drink anything for 8 to 14 hours before your test. You will be asked to drink a liquid that contains glucose . You will have blood drawn before you drink the liquid, and again 2 more times every 60 minutes after you drink it. Each time, your blood glucose level will be checked. Allow at least 2 hours for this test.Continue reading > >
You May Like: What Food To Eat To Break Intermittent Fasting
When Things Go Awry
When we eat food, the pancreas goes to work, releasing enzymes that help to break down food and hormones that help the body handle the influx of glucose. One of these hormones is insulin, and it plays a key role in managing glucose levels in the blood.
And here is where things can go wrong. If the pancreas doesnt make enough insulin or stops making it altogether, in the case of type 1 diabetes glucose levels in the blood can rise too high. Another scenario is that the pancreas makes enough insulin but the cells have trouble using it properly, causing blood glucose levels to rise. This is called insulin resistance and is the hallmark of type 2 diabetes.
In the short term, high blood glucose levels can make you feel downright bad. Thirst, frequent trips to the bathroom, fatigue and weight loss are all symptoms of high blood glucose . If not treated, more serious issues can occur, such as diabetic ketoacidosis. Chronic high blood glucose levels can lead to complications such as heart, kidney and eye disease, as well as nerve damage. So, its all about the blood glucose.
A Warning Of Developing Type 2 Diabetes
Impaired fasting glycaemia is sometimes called pre-diabetes. This is when blood glucose levels in the body are raised, but are not high enough to mean that the person has diabetes. IFG means that the body isnt able to use glucose as efficiently as it should. This is because a layer of fat around the cells of the body, prevents insulin doing its job and taking the glucose into the cells of the body where its needed for energy. This situation is reversible by losing weight and hence the fat around the cells disappears. If you dont lose weight however, is it unlikely that you wont eventually develop Type 2 Diabetes.
IFG has no symptoms and can often go undiagnosed for years. Although there are no symptoms, many people diagnosed with IFG are overweight. Nine out of 10 people with IFG have high blood pressure, raised cholesterol levels or a family history of the condition.
IFG can lead to the development of type 2 diabetes. People with IFG are five to 15 times more likely to develop type 2 diabetes than people with normal glucose levels. However, this isnt inevitable. You can take steps to reduce the chances of this happening. People with IFG also have a slightly increased risk of heart disease and stroke.
Also Check: What Should You Eat When Doing Intermittent Fasting
Living With Type 1 Diabetes:
Life with type 1 diabetes poses lifelong challenges for every member of the family.
People with type 1 diabetes should:
- Test blood glucose levels three or more times per day and adjust their insulin through injections or an insulin pump.
- Ensure insulin doses are balanced with food intake and level of daily activity. People with type 1 diabetes may experience low and high blood sugar levels, which should be carefully monitored and managed.
While living with type 1 diabetes requires a certain amount of daily structure, newer pumps and insulin products have provided more flexibility in the management of this condition.
A healthcare provider can provide advice to help properly manage blood glucose levels.
How Do I Prepare For The Plasma Glucose Level Test And How Are The Results Interpreted
To get an accurate plasma glucose level, you must have fasted for at least 8 hours prior to the test. When you report to the clinic or laboratory, a small sample of blood will be taken from a vein in your arm. According to the practice recommendations of the American Diabetes Association, the results of the blood test are interpreted as follows:
Fasting blood glucose level
- If your blood glucose level is 70 to 99* mg/dL . . .
- What it means: Your glucose level is within the normal range
*Values between 50 and 70 are often seen in healthy people
**The condition of “prediabetes” puts you at risk for developing Type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and blood lipid disorders
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 02/21/2018.
References
You May Like: How To Do 16 8 Fasting
Know And Improve Your Fasting Glucose By Testing
Its best to test and not to guess. Knowing your blood sugar level will help you optimize it. InsideTracker provides the tools for you to reach your optimal fasting glucose level so you can preserve your mood, sleep, and cognition. Even better, repeated testing with InsideTracker can reveal your blood sugar trends. Optimize your fasting blood sugar so that you can take control and set yourself up for a high-performance future.
Other Types Of Glucose Testing
Random glucose testing isnt a substitute for your normal glucose testing schedule. You should also perform fasting tests and tests after meals, as suggested by your doctor.
A fasting blood glucose test is usually performed upon waking, before you eat. Testing after meals measures glucose levels around two hours after the start of a meal. Different testing times will yield different results. These are affected by:
- the food youve eaten
- medications youre taking
- any exercise youve done
For some people, its important to test every day. This helps you get a sense of your overall blood sugar control and can help you make treatment decisions. Testing is the best way to learn how your blood sugar is affected by your lifestyle, medications, or both.
Also Check: What Do You Eat When You Do Intermittent Fasting
Is Diabetes More Common In Men Or Women
Studies show that type 1 diabetes is more common in men, and theyre more likely to pass it on to their offspring. However, although women previously showed more indication of type 2 diabetes, it is now equally prevalent between men and women.
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition that usually starts in childhood. With type 1 diabetes, your body attacks its own pancreas so it cannot produce insulin. Type 2 diabetes is far more common in adults, and although often milder than type 1, can still cause major health implications, including kidney disease or damage, heart disease, or stroke. Unlike type 1, with type 2 diabetes some insulin can be produced, but the body is either resistant to it or there is not enough. This insulin resistance develops in fat, liver, and muscle cells, hence the extensively researched correlation between obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Fasting Plasma Glucose Test
A fasting plasma glucose test is taken after at least eight hours of fasting and is therefore usually taken in the morning.
The NICE guidelines regard a fasting plasma glucose result of 5.5 to 6.9 mmol/l as putting someone at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes, particularly when accompanied by other risk factors for type 2 diabetes.
Don’t Miss: What Can You Eat On Fasting
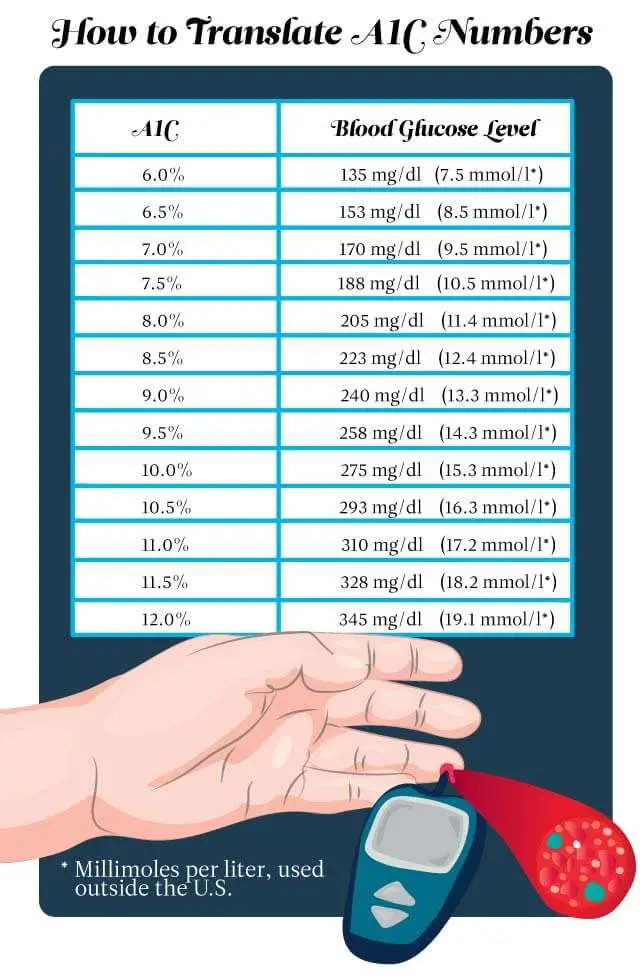
What Is Hemoglobin A1c
Hemoglobin A1C is a lab test. It indicates an average blood glucose reading for the last 90 days. It is done when you find out you have diabetes, and every 3 months after that at clinic visits. A person without diabetes has a Hemoglobin A1C of less than 5.6%.
|
Target Hgb A1C is 7.5% for all children and adults with diabetes. |
The chart below shows the Hemoglobin A1C result compared with the blood glucose number.
Why Do We Care About Blood Glucose Levels
Glucose is one of the rare molecules in our body where we can and should monitor our current levels. For example, we dont talk about our levels of amino acids or triglycerides nearly as much. Thats for a few reasons:
Don’t Miss: What Kind Of Fasting Should I Do
What Is A Fasting Blood Sugar Test
A fasting blood glucose test, also known as a fasting plasma glucose test or fasting blood sugar test, is a method for measuring the amount of glucose in the blood after a period of fasting. Most commonly, fasting occurs overnight and the test is performed first thing in the morning.
There are two primary purposes of a fasting blood glucose test:
- To diagnose diabetes
- To understand how different factors affect your blood sugar throughout the day
A fasting blood glucose measurement can be taken by a healthcare professional by blood draw and sent to a lab, or as a fingerstick test performed at home. The two processes are testing the same thing, so they are often referred to in the same way. A healthcare professional may order a lab test to eliminate other variables that may come into play with a fingerstick test, such as substances on the hand or not using a large enough blood drop.
If your healthcare team suspects that you may have prediabetes or type 2 diabetes, they may perform a fasting plasma glucose test or an A1C test. If you have already been diagnosed with diabetes, checking your fasting blood sugar level in the morning gives you a baseline blood sugar reading for your day. These tests can be performed at home as recommended by your healthcare team, using a blood glucose meter. However, the at-home blood glucose meter testing method is not intended for the diagnosis of diabetes.
Related Reading: Blood Sugar Levels: What is Normal, Low or High, Target Ranges & More
How Low Should Your Blood Glucose Be In Ketosis
Many people embark on a ketogenic diet in the hope of managing their diabetes and lose weight. They want lower insulin levels to enable them to burn more body fat for long-term insulin sensitivity and health.
On the left-hand side of the total energy chart below, we have endogenous ketosis . With lower levels of energy in your blood, your body will draw on your fat stores to make up the difference, as well as using excess stored fat and old proteins in your liver, pancreas, brain and other organs . This is a great place to be if you are trying to reduce your blood sugar or lose body fat.
Also Check: How To Do Low Carb Intermittent Fasting
Your Blood Sugar Isnt Just Because Of What You Eat
Mainstream media would have you believe that your blood sugar levels are impacted only by what you eat and how much you exercise, but people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes who test their blood sugars frequently could tell you otherwise.
Its especially important to keep this mind when looking at your own blood sugars and your goals because there are certain variables and challenges that impact blood sugar levels that you cant always control.
For example:
- Menstrual cycles: raises blood sugar and insulin needs
- Adrenaline rushes from competitive sports, heated arguments, rollercoaster rides: raises blood sugar and insulin needs
- The common cold and other illnesses: usually raises blood sugar and insulin needs
- Hormonal changes due to puberty and healthy growth in young adults: raises blood sugar and insulin needs
- An injury which raises overall inflammation levels: raises blood sugar and insulin needs
- Glucogenesis during anaerobic exercise: raises blood sugar
While you cant necessarily prevent these factors that affect your blood sugar from occurring, you can work with your diabetes healthcare team to adjust your insulin, other diabetes medications, nutrition and activity levels to help compensate for them when they do occur.
For example, when engaging in anaerobic exercise like weightlifting many people with type 1 diabetes find it necessary to take a small bolus of insulin prior to or during their workout because anaerobic exercise can actually raise blood sugar.
How Low Should Your Blood Sugars Be For Optimal Ketosis
According to mainstream medical definitions:
- normal blood sugar is defined as having an HbA1c of less than 6.0%,
- Prediabetes occurs when you have an HbA1c between 6.0 and 6.4%, and
- Type 2 diabetes is diagnosed when you have an HbA1c of 6.5% or above.
However, these mainstream definitions of normal are far from optimal! Your risk of diabetes, stroke, heart disease, cardiovascular disease and cancer increase with an HbA1c above 5.0%.
By the time you have prediabetes, you have an increased risk of many of the most common western diseases of ageing .
However, simply lowering your blood sugars using medications does not necessarily reduce your risk.
If youre interested in pursuing optimal rather than what passes as normal metabolic health, the table below shows suggested HbA1c and blood sugar targets based on the risk categories for stroke, cardiovascular disease and heart disease shown in the charts above.
Also Check: What Is Fasting To Lose Weight
What Are Target Blood Sugar Levels For People With Diabetes
A target is something that you aim for or try to reach. Your health care team may also use the term goal. People with diabetes have blood sugar targets that they try to reach at different times of the day. These targets are:
- Right before your meal: 80 to 130
- Two hours after the start of the meal: Below 180
Talk with your health care team about what blood sugar numbers are right for you.