Is Fasting Good For Diabetes
Research has shown that intermittent fasting may be beneficial. It may lower blood glucose levels , blood insulin, and HgbA1c, but there are side effects and potential risks. And, although the research is promising for intermittent fasting and diabetes, additional research should be done in more populations and for longer periods of time.
Intermittent Fasting And Type 1 Diabetes
Intermittent fasting for the management of type 1 diabetes is much more difficult and significantly increases the individuals risk of hypoglycemia. While the benefits of intermittent fasting may extend to type 1 diabetics, this eating method should only be done under the guidance of your health practitioner. There are also limited clinical trials on fasting diets and the effects on the health of people with type 1 diabetes to ascertain the long-term effects.
How Long Can A Person With Diabetes Go Without Eating
If you choose to adopt a form of intermittent fasting to help manage diabetes, this question/decision is why it is vitally important to speak with your doctor before starting. Not only do you need to consider what is safe for you, your mental health, and your diabetes management but also what is practical for your lifestyle and needs. Your healthcare team should be involved in this decision.
Also Check: How To Do 12 Hour Fasting
History Of Diabetes And Intermittent Fasting
Fasting has been around for a long time. It’s been a historical part of some spiritual traditions stretching back centuries. More recently, IF has been used as part of a healthy diet for weight loss, as a “detoxifying” strategy, and more.
There’s been some debate about whether fasting is healthy for those with diabetes. A growing body of evidence suggests that some IF diets could benefit people with diabetes. Scientists note that when a person fasts may be just as important as the diet itself.
Drawbacks Of Intermittent Fasting For Diabetes

One of the major drawbacks with intermittent fasting is hypoglycemia low blood sugar. Especially if youre taking insulin, sulfonylureas or drugs that increase insulin secretion from the beta cells of the pancreas, its important that you work closely with your doctor and diabetes care team before you decide to go the intermittent fasting route.
Our body has a unique way of handling a lack of food or decreased intake in our system. One way is a hormonal response, where insulin levels stay low. Other hormonal changes during times of intermittent fasting include increased HGH , and increased release of the fat burning hormone norepinephrine fasting.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Best Fasting Window
Trying A Different Approach To Intermittent Fasting
Fast-forward to this year. After being more sedentary than ever during the quarantine, I needed something to switch up my routine. I decided to try intermittent fasting one more time.
However, this time I looked at a different model: the Warrior Diet. There isnât much research specifically backing up this approach to intermittent fasting, but I thought that with some modifications, it might work for me.
Empowered by my previous experience and knowledge of how I responded to different foods and eating at various times of the day, I decided to modify the plan for myself right from the start.
Rather than eating a large meal at night, I had my largest meal as a midafternoon meal . Rather than fight against my own usual body rhythm, I decided to work with it so the plan would be more sustainable for me.
The other part that made it more workable for me was that during the rest of the day I could munch on small amounts of raw fruits and vegetables.
I returned to my previous strategy of testing my blood sugar six times a day and, with this method, I never experienced a hypoglycemic event.
I began to lose small amounts of weight, about a half-pound to a pound per week. After 3 months on this plan, my A1C also decreased. Seeing the lower A1C felt like a big win!
Since it feels natural and matches my own body rhythm, Iâm not feeling deprived at all, and Iâve also noticed an increase in energy.
Can Intermittent Fasting Treat Diabetes
The evidence for IF treating type 2 diabetes is promising but preliminary. Lets review a few data points:
- A 2021 review looked at seven randomized controlled trials using IF to treat type 2 diabetes. Compared to a regular eating program, IF was associated with greater weight loss but reductions in blood sugar were not observed.
- A 2018 study found that 5:2 intermittent fasting led to significant blood sugar reductions in people with type 2 diabetes.
- A 2018 review of four studies found that IF was effective for weight loss irrespective of BMI.
- Dr. Jason Fung has successfully treated diabetes with therapeutic fasting in his Toronto clinic.
Fasting may also help with other forms of diabetes:
- Researchers believe that time-restricted feeding may effectively prevent type 2 diabetes and prediabetes, but more research is needed.
- Intermittent fasting led to significant weight loss in women with a history of gestational diabetes.
- People with type 1 diabetes fasted safely during Ramadan with proper glucose monitoring.
Lets talk more about IF risks now.
Also Check: What Is The Best Form Of Intermittent Fasting
Popular Intermittent Fasting Methods
- The 16/8 method: Each day you fast for 16 hours and consume all your daily eating during the other 8 hours. It is also called the Leangains protocol.
- The 5:2 diet: In a week, you eat normally for 5 days and on the other 2 days you eat no more than 500 to 600 calories. It is also called the fast diet.
- Warrior Diet: For 20 hours each day, you restrict your caloric intake to only water, noncaloric drinks, and small amounts of raw veggies and fruit. During the other 4 hours, you eat a very large dinner. For all intakes, the method encourages eating unprocessed food.
Before trying it, one of my concerns was that I would end up in a hypoglycemic state, not just based on the reading, but because this had been a personal challenge. When I was initially diagnosed, I was struggling with both extreme highs and lows. The number of times I had blood sugars below 50 even seemed to stump my doctors.
I decided not to try the fast diet because I like structure and routines. Having 2 days of the week being drastically different while also juggling my family and career, sounded unsustainable.
I was committed to trying something new and didnât want to set myself up for failure, so I decided to try the Leangains protocol.
While it required 16 hours of fasting a day, in my mind, 8 of those hours didnât count because that would be wind-down and sleeping time when I wouldnât have been eating anyway. Thus, I thought it would be the least likely to push me toward extremely low blood sugars.
Editorial Sources And Fact
- Fothergill E, Guo J, Howard L, et al. Persistent Metabolic Adaptation 6 Years After The Biggest Loser Competition. Obesity. August 2016.
- Varady KA, Cienfuegos S, Ezpeleta M, et al. Cardiometabolic Benefits of Intermittent Fasting. Annual Review of Nutrition. October 2021.
- Gabel K, Hoddy KK, Haggerty N, et al. Effects of 8-Hour Time Restricted Feeding on Body Weight and Metabolic Disease Risk Factors in Obese Adults: A Pilot Study. Nutrition and Healthy Aging. June 2018.
- Catterson JH, Khericha M, Dyson MC, et al. Short-Term, Intermittent Fasting Induces Long-Lasting Gut Health and TOR-Independent Lifespan Extension. Current Biology. June 2018.
- De Cabo R, Mattson MP. Effects of Intermittent Fasting on Health, Aging, and Disease. The New England Journal of Medicine. December 26, 2019.
Also Check: Best Diet Plan For Intermittent Fasting
Impact Of Intermittent Fasting On Additional Metabolic Parameters
To further evaluate the metabolic impact of IF interventions compared to a standard diet, we pooled the data of studies that assessed changes in fasting glucose, lipid profile, blood pressure, and waist circumference. IF was not associated with additional positive effects on any of these parameters compared to a standard diet .
Meta-analysis comparing metabolic parameters between intermittent fasting interventions and standard diet in patients with type 2 diabetes
| Clinical characteristic . |
|---|
Which Fasting Plan Is Best
The term intermittent fasting does not refer to a single well-defined practice. Several different approaches fall under the intermittent fasting umbrella. The three most common and well-studied are known as time-restricted eating, alternate-day fasting, and the 5:2 diet.
The first of thesetime-restricted eatinginvolves squeezing all of your days calories into a single feeding window of six to eight hours. For example, someone on this diet may eat between noon and 6 p.m. each day, and avoid all caloric foods and drinks for the other 18 hours of the day. Meanwhile, someone on an alternate-day-fasting diet eats normally one day, but the next day consumes few or no calories. Finally, the 5:2 diet involves eating normally five days a week but fasting on the other two days.
There are many variations of each of these plans. At this point, its unclear which of these, if any, is optimal for people with Type 2 diabetes. I think time-restricted eating is probably the most common, followed by fasting two days a week, Horne says. But at the moment, I would say there is not one plan that stands out as a best option. The right plan, he adds, is the one a patient will stick with. Even if the more intense fasting programs turn out to be most beneficial, that doesnt really matter if people cant adhere to it.
Read More:The Link Between Type 2 Diabetes and Psychiatric Disorders
Recommended Reading: What Can I Drink During Fasting
Why Might Changing Timing Help
But why does simply changing the timing of our meals to allow for fasting make a difference in our body? An in-depth review of the science of IF recently published in New England Journal of Medicine sheds some light. Fasting is evolutionarily embedded within our physiology, triggering several essential cellular functions. Flipping the switch from a fed to fasting state does more than help us burn calories and lose weight. The researchers combed through dozens of animal and human studies to explain how simple fasting improves metabolism, lowers blood sugar levels lessens inflammation, which improves a range of health issues from arthritic pain to asthma and even helps clear out toxins and damaged cells, which lowers risk for cancer and enhances brain function.
Can Intermittent Fasting Cure Type 2 Diabetes
Question: I have type 2 diabetes and Ive heard that intermittent fasting could cure me. Is this true?
Answer: In recent years, intermittent fasting has emerged as a novel way of treating patients with type 2 diabetes. There are anecdotal reports of patients who have lost weight, their blood sugar levels have improved significantly, and they no longer need to take their diabetes medications. Their disease appears to be in remission if not exactly cured.
However, endocrinologists the doctors who routinely treat diabetes as well as dietitians, are skeptical. They point to a lack of major studies that prove this approach is effective and safe long term. After all, intermittent fasting requires a big change in eating habits and it remains to be seen how many people can stick with it.
The first thing you need to know is that there are different ways of doing intermittent fasting which is basically not eating for certain periods of time.
For instance, you could restrict your consumption of food to just eight hours a day say from 11 a.m. to 7 p.m. and eat nothing else for the other 16 hours.
Or, you might have just one meal a day and then fast for 24 hours.
Another approach is to eat normally on some days of the week, while significantly curbing calories on other days.
Fasting has been part of human culture for thousands of years. Most of the major religions encourage their believers to restrict food intake during certain times.
Recommended Reading: What To Eat While Intermittent Fasting 16 8
Staying Well While Fasting
If you decide to fast, it is important to test your blood glucose levels more often as your blood sugar levels after fasting eight hours may drop too low . This is more likely to happen if you are unwell, treat your diabetes with insulin or some diabetes medications, or both. Speak to your diabetes team about this.
If you experience the symptoms of a hypo, such as feeling shaky, sweaty and disorientated, you must break the fast immediately and treat it with your usual hypo treatment, like glucose tablets, a sugary drink or GlucoGel, followed by a snack such as a sandwich or a bowl of cereal.
If you have to break your fast for any reason, continue your meals as normal for that day. You may be able to make up the fast at a later date or provide meals to the needy.
If you have type 1 diabetes, there is also a danger that your blood glucose levels may run too high and result in a build-up of ‘ketones’. This could potentially result in a serious condition known as ketoacidosis. The symptoms of high blood glucose levels might include feeling very thirsty, passing a lot of urine or extreme tiredness. If your blood glucose levels stay high and you experience these symptoms, speak to your healthcare team.
Should You Consider Intermittent Fasting
If you have type 2 diabetesand especially if you have challenges managing your blood sugar, you require insulin therapy, or are taking numerous type 2 diabetes medicationsit is advised to consult with a health care provider before entering any intermittent fasting program that is not supervised by medical experts. If you follow an intermittent fasting program, its also important that your blood sugar levels are carefully monitored, as you may be able to lower or even stop your insulin therapy or type 2 diabetes medications.
Don’t Miss: Body Types And Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent Fasting And Insulin Sensitivity
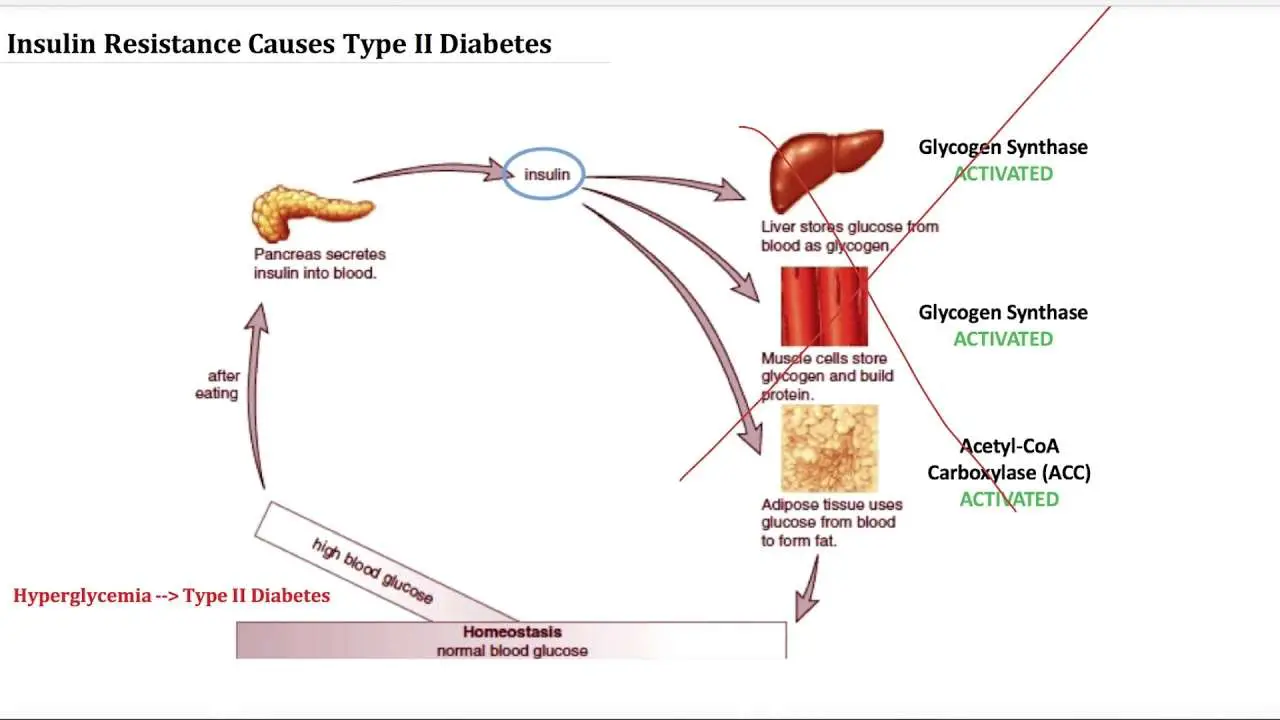
Insulin plays a significant role in glucose homeostasis due to its influence in promoting the storage and utilization of glucose. However, the effects of insulin are not limited to glucose homeostasis. Insulin also plays a role in the stimulation of DNA synthesis, RNA synthesis, cell growth and differentiation, amino acid influx, protein synthesis, inhibition of protein degradation, and most importantly, the stimulation of lipogenesis and inhibition of lipolysis .
It is the development of insulin resistance, which is defined as the necessity of higher circulating insulin levels in order to produce a glucose lowering response, that is thought to be responsible for the development of type 2 diabetes . In order to promote regulation of glucose homeostasis, insulin works primarily on receptors in skeletal muscle, liver, and white adipose tissue . In short, there are several proposed mechanisms regarding the development of insulin resistance. One of the more prominent theories describes the association of increased adiposity and the subsequent chronic inflammation that leads to the development of insulin resistance in tissues .
I Tried Intermittent Fasting For Diabetes And This Is What Happened
Content created for the Bezzy community and sponsored by our partners. Learn More
â¢â¢â¢â¢â¢
Grant Tinsley, Ph.D., CSCS,*D, CISSN
Medically Reviewed
â¢â¢â¢â¢â¢
â¢â¢â¢â¢â¢
â¢â¢â¢â¢â¢
Grant Tinsley, Ph.D., CSCS,*D, CISSN
Medically Reviewed
â¢â¢â¢â¢â¢
â¢â¢â¢â¢â¢
My experience reinforced that there is no one-size-fits-all approach to diabetes management.
If youâve ever tried to lose weight, especially for health reasons, you have probably come across articles and blog posts touting the benefits of intermittent fasting.
Itâs also known as intermittent energy restriction in dietitian, nutritionist, and health coach circles. Regardless of which term you use, intermittent fasting is a method of voluntarily cycling between fasting and nonfasting time periods.
I started reading about it a few years ago, because I heard it was helpful for those with type 2 diabetes.
Reported benefits include weight loss and a lower risk of future diabetes complications, such as organ damage. The thought process around this is that if you reduce your time periods of high blood sugar, then you reduce the potential for damage caused by long-term unmanaged type 2 diabetes.
In one 2013 study in the British Journal of Nutrition, women with overweight who tried intermittent fasting not only lost weight but improved insulin sensitivity after 3 months.
Recommended Reading: What Do You Eat With Intermittent Fasting
Effects Of Intermittent Fasting On Health Markers In Those With Type 2 Diabetes: A Pilot Study
Correspondence to: Kerry D Mansell, BSP, PharmD, MBA, Associate Professor, Division of Pharmacy, College of Pharmacy and Nutrition, University of Saskatchewan, 104 Clinic Place, Saskatoon, SK S7K 5E5, Canada.
Telephone: +1-306-9665235 Fax: +1-306-9666377
How Does Intermittent Fasting Work With Type 2 Diabetes
According to an academic review,² 24-hour fasting regimens significantly reduced weight and blood glucose in people with diabetes. These diets also led to some patients stopping insulin therapy as their blood sugar was under control.
Researchers noted that people might struggle with fasting for 24 hours or more. Therefore, they may be better off starting with shorter intervals and time-restricted feeding. They recommended this IF prescription:
-
In week one, fast for 12 hours and feed for 12 hours. Stick with this fasting period until you’re comfortable moving to the next phase. The researchers recommend monitoring and logging your daily blood glucose levels so you can send them to your doctor weekly.
-
Typically starting in week five, you fast for 16 hours and feed for eight hours. The next phase is to increase your fasting period by four hours when you’re ready. The report says that you should continue monitoring and logging blood sugar levels. You should also consult a registered dietician to discuss food intake and ensure you’re dieting responsibly.
-
Typically starting in week seven, you fast for 18-20 hours and feed for 4-6 hours. Finally, when you’re ready to continue to the next step of the IF process, it is time to add 2-4 more hours to your fasting routine. At this time, the report notes that your doctor should adjust your diabetes medication dosages based on your logged blood sugar readings.
Also Check: How Much Weight Can You Lose In 2 Weeks Fasting
