Eat Healthy Foods And Follow A Regular Eating Schedule
Following a healthy diet as recommended by your diabetes team, watching portion sizes, and not skipping meals can help to prevent side effects like low blood sugar that can occur while taking glipizide. Notify your healthcare providers if you are not able to eat because you are sick or because you will be having a surgery or procedure done.
The Impact Of Hormones
Hormones can have an impact on your fasting glucose levels. Hormones like cortisol and growth hormone are released in the morning to get your body ready for the day ahead. These also increase glucose levels.
Usually your body counteracts these by releasing some insulin to help keep your glucose levels within a tight bandwidth. In type 2 diabetes, insulin is being released but its not working very well. This leaves your glucose levels susceptible to rising above normal levels.
This can be difficult to control but it still represents an inability of your body to control its own glucose levels. Without diabetes, your fasting glucose levels would not go high at any time throughout the day. Therefore, this too represents a progression of the disease.
A Warning Of Developing Type 2 Diabetes
Impaired fasting glycaemia is sometimes called pre-diabetes. This is when blood glucose levels in the body are raised, but are not high enough to mean that the person has diabetes. IFG means that the body isnt able to use glucose as efficiently as it should. This is because a layer of fat around the cells of the body, prevents insulin doing its job and taking the glucose into the cells of the body where its needed for energy. This situation is reversible by losing weight and hence the fat around the cells disappears. If you dont lose weight however, is it unlikely that you wont eventually develop Type 2 Diabetes.
IFG has no symptoms and can often go undiagnosed for years. Although there are no symptoms, many people diagnosed with IFG are overweight. Nine out of 10 people with IFG have high blood pressure, raised cholesterol levels or a family history of the condition.
IFG can lead to the development of type 2 diabetes. People with IFG are five to 15 times more likely to develop type 2 diabetes than people with normal glucose levels. However, this isnt inevitable. You can take steps to reduce the chances of this happening. People with IFG also have a slightly increased risk of heart disease and stroke.
Recommended Reading: How To Get Electrolytes While Fasting
Randomized Controlled Trials In Healthy Volunteers
Who Should Do The Test
According to the American Diabetes Association, screening for diabetes is recommended in people over 45 , or at any age if you have certain risk factors, including :
- Being overweight, obese, or physically inactive
- Having a close relative with diabetes
- Belonging to a certain race/ethnic group
- Having signs of insulin resistance or conditions associated with insulin resistance, such as high blood pressure , low good cholesterol and/or high triglycerides , and polycystic ovary syndrome
- Having had diabetes in pregnancy
Also Check: How To Reduce Fasting Glucose
Managing Blood Sugar When Youre Ill
When you get sick, your blood sugar levels may fluctuate and become unpredictable.
If youre sick, its very important that you:
- drink plenty of water or sugar-free fluids
- check your blood sugar levels more often than usual
- take 15 grams of carbohydrate every hour if you are not able to follow your usual meal plan
- replace food with fluids that contain sugar if you cant eat solid food
- continue to take your insulin or other diabetes medication
If you have a cold or flu and want to use a cold remedy or cough syrup, ask your pharmacist to help you make a good choice. Many cold remedies and cough syrups contain sugar, so try to pick sugar-free products.
As an extra precaution, you should always check with your health-care team about guidelines for insulin adjustment or medication changes during an illness.
What Happens During The Test
Most people can take an A1C test at any time without preparing beforehand. However, a doctor may sometimes request that a person avoids eating or drinking for 8 hours before the test.
Women who are pregnant may need to drink a sugary beverage 1 hour before the test.
A doctor or nurse will collect a blood sample, usually from a vein in the arm or hand. They will send the sample to a laboratory for analysis.
Read Also: What Can You Have To Drink During Intermittent Fasting
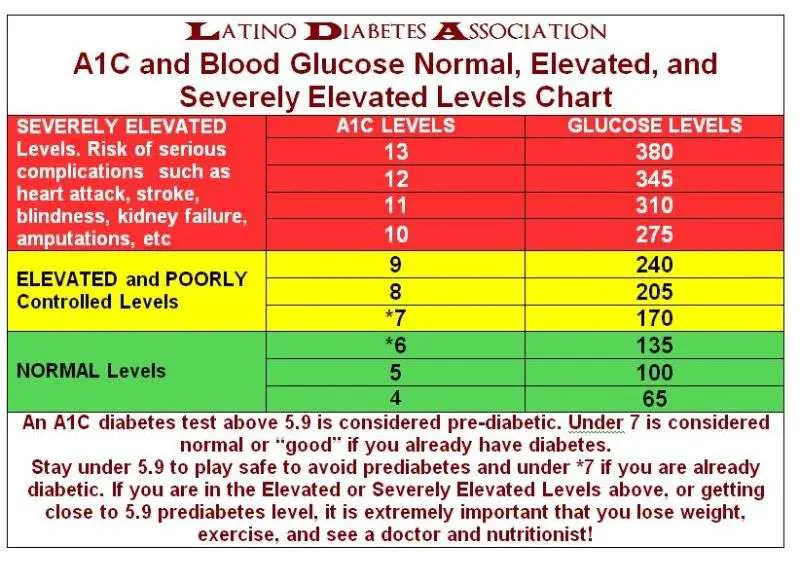
Summary Of Normal Glucose Ranges
In summary, based on ADA criteria, the IDF guidelines, a persons glucose values are normal if they have fasting glucose < 100 mg/dl and a post-meal glucose level < 140 mg/dl. Taking into account additional research performed specifically using continuous glucose monitors, we can gain some more clarity on normal trends and can suggest that a nondiabetic, healthy individual can expect:
- Fasting glucose levels between 80-86 mg/dl
- Glucose levels between 70-120 mg/dl for approximately 90% of the day
- 24-hour mean glucose levels of around 89-104 mg/dl
- Mean daytime glucose of 83-106 mg/dl
- Mean nighttime glucose of 81-102 mg/dl
- Mean post-meal glucose peaks ranging from 99.2 ± 10.5 to 137.2 ± 21.1 mg/dl
- Time to post-meal glucose peak is around 46 minutes 1 hour
These are not standardized criteria or ranges but can serve as a simple guide for what has been observed as normal in nondiabetic individuals.
High Blood Sugar Symptoms
Hyperglycemia is the medical term for high blood sugar. Hyperglycemia happens when the body doesnt have enough insulin or when it cant use insulin correctly. Many things can cause high blood glucose levels like Type 1 diabetes, Type 2 diabetes, stress, illness, or the dawn phenomenon. If you have hyperglycemia or suspect you may have it, talking with a healthcare provider is always a good idea. A doctor can help you determine whats causing your high blood sugar levels and lower it to a healthy range.
Here are some of the most common symptoms that may indicate hyperglycemia:
- Fatigue
- Vision loss
You should seek immediate medical attention if your blood sugar reaches 400 mg/dL or higher.
When patients experience any of these accompanied by elevated blood sugar levels, diabetic patients are advised to go directly to the ER to avoid diabetes-induced coma, says Vikram Tarugu, MD, a gastroenterologist and the CEO of Detox of South Florida. Patients who have elevated blood sugar may also present with frothy, ketone-like smelling breath.
Here are some lifestyle changes and medical treatments that can help treat hyperglycemia:
Don’t Miss: What Vitamins Should I Take While Fasting
Causes Of Impaired Fasting Glycaemia
IFG develops if your body becomes unable to control glucose levels. Your body may be unable to use insulin properly or produce less insulin. There are a number of factors that may make you more likely to develop IFG. If youre black or South Asian and over 25, or if youre white and over 40, and you have one or more of the following risk factors, then you may be at risk of IFG:
- one of your parents, brother or sister has type 2 diabetes
- youre overweight or you carry extra weight around your middle rather than your hips and thighs
- you have high blood pressure or you have had a heart attack or stroke
- you have polycystic ovary syndrome and you are overweight
- you have had diabetes during pregnancy
- you have severe mental health problems
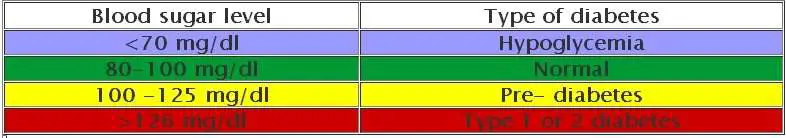
What Do The Test Results Mean
- If your fasting blood glucose level is between 3.6mmol/l and 6mmol/l, this means that your blood glucose level is normal.
- If your fasting blood glucose level is 7mmol/l or higher, this is likely to mean that you have diabetes. Diabetes is a long-term condition where the body is not able to control the amount of glucose in the blood.
- If your fasting blood glucose level is between 6.1mmol/l and 6.9mmols/l, you may have IFG.
Also Check: What Is Fasting To Lose Weight
Cgm Studies In Nondiabetic Individuals
One study from 2009 entitled Reference Values for Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Chinese Subjects looked at the glucose levels of 434 healthy adults using CGM and found the following:
- On average, their daily glucose levels stayed between 70140 mg/dl for 93% of the day, with very small portions of the day spent above 140 mg/dl or below 70 mg/dl.
- Also, their mean 24-hour glucose levels were around 104 mg/dl
- 1-hour post-meal glucose values average 121-123 mg/dl for breakfast, lunch, and dinner
- 3-hour post-meal glucose values were around 97-114 mg/dl.
- Peak post-meal values appeared to be around 60 minutes after eating.
- Mean fasting glucose was 86 ± 7 mg/dl.
- Mean daytime glucose was 106 ± 11 mg/dl.
- Mean nighttime glucose was 99 ± 11 mg/dl.
A 2010 study, Variation of Interstitial Glucose Measurements Assessed by Continuous Glucose Monitors in Healthy, Nondiabetic Individuals, looked at a healthy population of 74 individuals that included children, adolescents, and adults during daily living using CGM. This research showed that:
- Glucose levels stayed between 71-120 mg/dl for 91% of the day.
- Levels were lower than 70 mg/dl for 1.7% of the time and greater than 140 mg/dl, only 0.4% of the time.
- Mean 24-hour glucose was 98 ± 10 mg/dl.
- Mean fasting glucose of 86 ± 8 mg/dl.
Compared to the first study mentioned, these healthy, nondiabetic individuals appeared to have a tighter range of glucose, spending the vast majority of the 24-hour period between 71-120 mg/dl.
How Do I Prepare For The Plasma Glucose Level Test And How Are The Results Interpreted
To get an accurate plasma glucose level, you must have fasted for at least 8 hours prior to the test. When you report to the clinic or laboratory, a small sample of blood will be taken from a vein in your arm. According to the practice recommendations of the American Diabetes Association, the results of the blood test are interpreted as follows:
Fasting blood glucose level
- If your blood glucose level is 70 to 99* mg/dL . . .
- What it means: Your glucose level is within the normal range
*Values between 50 and 70 are often seen in healthy people
**The condition of “prediabetes” puts you at risk for developing Type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and blood lipid disorders
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 02/21/2018.
References
Recommended Reading: Can You Eat Anything On Intermittent Fasting
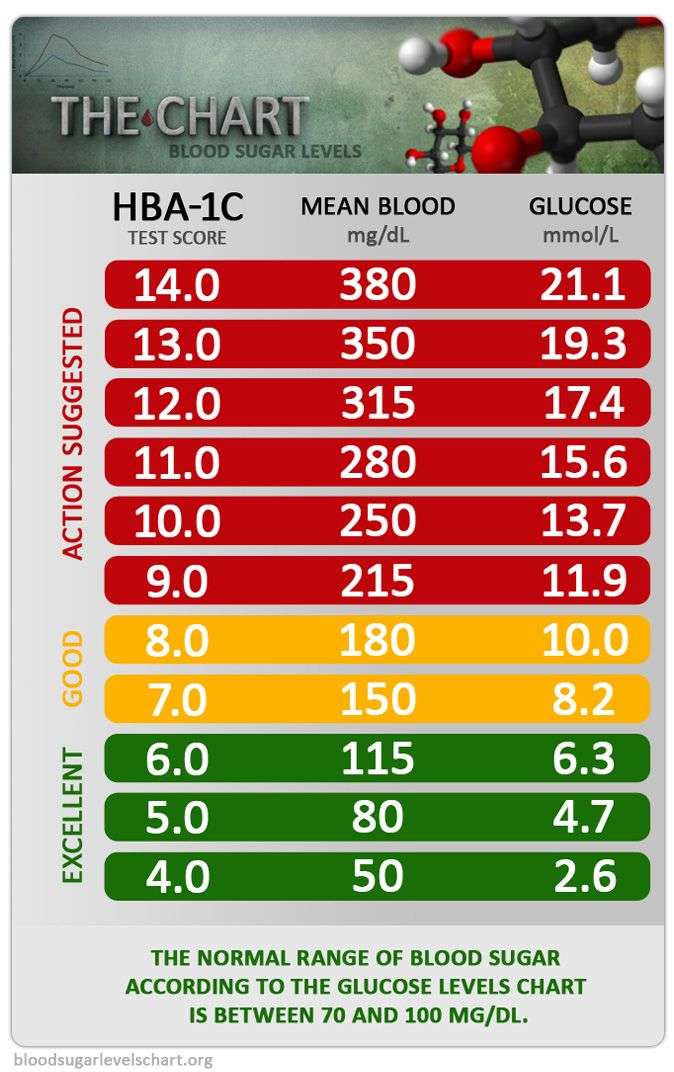
Chart For Normal Fasting Blood Sugar Levels
| TAKE-HOME TIPS |
Normal fasting blood sugar levels are considered fasting blood sugar levels between 80 mg/dl and 100 mg/dl. However, nowadays, this normal range is changed due to different reference ranges of laboratories use.
These figures come out when you measure your blood sugar level in the morning after have been fasting for at least 8 hours.
This is the time between the dinner and your breakfast. Everything you eat influence in you fasting blood sugar level.
What you need to do is to keep your fasting blood sugar levels at a normal range, I.e as lowest as possible. If you find it so difficult for you, let our specialized medical team do the job.
Blood Sugar Level Chart
- Normal reading for nondiabetic person = 7099 mg/dl
- The recommendation for someone who is diabetic = 80130 mg/dl
Two hours after a meal
- Normal reading for nondiabetic person = Below 140 mg/dl
- The recommendation for someone who is diabetic = Below 180 mg/dl
HbA1c
- Normal reading for nondiabetic person = Below 5.7%
- The recommendation for someone who is diabetic = 7% or less
**My Med Memo The measurement mmol is the abbreviation for millimole.
Read Also: How Many Calories Can I Have During Intermittent Fasting
Why Doctors Order It
A fasting blood glucose test is done to screen for prediabetes and diabetes. It also helps doctors monitor diabetes and determine if medications and dietary changes are having an effect .
Your fasting blood glucose level is the lowest your blood sugar can be because the influence of recent meals is minimized .
Fasting blood sugar is often checked alongside HbA1c , which is a measure of your blood sugar levels over the past three months. The more sugar there is in the blood, the more it will attach to hemoglobin, raising HbA1c .
Taken together, the two offer more information than each test alone. For example, even if your blood sugar levels are very high at one random point, they may have been mostly low over the past couple of months . On the other hand, HBA1c could be higher but your glucose levels at the moment lower.
Apart from diabetes, abnormal levels can point out issues such as insulin resistance, hormonal imbalances, and pancreatic, liver, or kidney disease.
Symptoms Treatments And Prevention
Hyperglycemia means high glucose in the blood . Your body needs glucose to properly function. Your cells rely on glucose for energy. Hyperglycemia is a defining characteristic of diabeteswhen the blood glucose level is too high because the body isn’t properly using or doesn’t make the hormone insulin.
Eating too many processed foods may cause your blood sugar to rise.
Read Also: Does Fasting Make Your Metabolism Faster
What Is High Blood Sugar
If your blood sugar levels are chronically higher than normal, then this is referred to as hyperglycaemia. This is a common issue for those suffering from diabetes. The condition can also affect pregnant women who have gestational diabetes and occasionally those who are severely ill .
Some of the symptoms of hyperglycaemia include:
- Increased thirst
- Blurred vision
- Issues with concentration and/or thinking
If severe hyperglycaemia is left untreated the condition can lead to organ and tissue damage as the excess glucose present in the body can make it difficult for the organs and cells to function correctly. The disorder can also impair the immune system response in the healing of wounds and cuts.
Why Would I Fast
There are many reasons you may want to fast. Some religions have fasting holidays or observances. Some medical procedures, like surgeries and certain blood work, require a fasted state.
Intermittent fasting has become quite popular recently as a weight loss tool. People doing this type of fast generally have normal fasting blood sugar levels and simply restrict their eating within a certain time period during the day. Intermittent fasting can take the form of alternate days fasted, time-restricted feeding, or periodic fasting, depending on the persons goals and body.
Read Also: What You Can Have During Intermittent Fasting
Who Is Most At Risk For Developing Diabetes
The following categories of people are considered “high-risk” candidates for developing diabetes:
- Individuals who are overweight or obese
- Individuals who are 45 years of age or older
- Individuals with first-degree relatives with diabetes
- Individuals who are African-American, Alaska Native, American Indian, Asia American, Hispanic/Latino, Native Hawaiian, Pacific Islanders,
- Women who developed diabetes while they were pregnant or gave birth to large babies
- Individuals with high blood pressure
- Individuals with high-density lipoprotein below 25 mg/dl or triglyceride levels at or above 250 mg/dl
- Individuals who have impaired fasting glucose or impaired glucose tolerance
- Individuals who are physically inactive engaging in exercise less than three times a week
- Individuals who have polycystic ovary syndrome, also called PCOS
- Individuals who have acanthosis nigricans — dark, thick and velvety skin around your neck or armpits
In addition to testing the above individuals at high risk, the American Diabetes Association also recommends screening all individuals age 45 and older.
What Causes Impaired Fasting Glucose
As stated, Impaired Fasting Glucose occurs when the body is not able to keep the sugar levels in the blood at a normal level resulting in above normal values for blood sugar consistently, especially when fasting causing Impaired Fasting Glucose. Biologically speaking, the sugar content in the food that we eat is used by the body for providing energy and is stored in the cells.
This function of storing the sugar in the cells is done by insulin which also controls the level of sugars in the blood and keeps it to normal. At times, what happens is that the insulin does not function the way it should or the insulin produced by the pancreas is not sufficient to absorb all the sugar content present in the body and store them in cells. This condition is called insulin resistance. This insulin resistance is what gives rise to increased levels of sugar in the blood causing Impaired Fasting Glucose or prediabetes.
People who lead a sedentary lifestyle, or are overweight, or have a family-history of diabetes are more prone to having Impaired Fasting Glucose or prediabetes which may ultimately progress to full blown diabetes mellitus.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Most Effective Intermittent Fasting Schedule
Looking To Get Tested
More than 500+ lab tests available online – confidential, convenient and affordable no doctors referral needed, no insurance required
- Secure and Confidential Results
- No Insurance or Referral Needed
- Affordable Pricing including Doctor’s Order
- 100% Satisfaction Guarantee
-
Online or over the phone
- 2
Find a Lab Near You
Over 3,500 locations to choose from
- 3
