Add More Spices To Your Food
Spicy foods may be difficult for you to consume, but they can help you with weight loss. Research suggests that spicy food can help boost your metabolism. Thats because hot peppers tend to have capsaicin.
Capsaicin speeds up your metabolism by speeding up your fat-burning mechanisms. Thus, you burn more fat and use that energy. Additionally, it can also help you suppress your appetite. Spicy foods make you feel fuller, so you will be eating less throughout the day.
In addition to weight loss, spicy foods also help with gut health. They help maintain a healthy gut microbiome. They also help reduce inflammation in the gut, which can help with obesity.
If you dont love spicy food, we recommend starting easy. Starting with ghost pepper and expecting to lose weight in a few days wont get you anywhere.
Furthermore, you should be careful only to consume natural spices added to healthy meals instead of adding hot sauces to your fast food. You should work on building a spice tolerance and then go from there.
Types Of Intermittent Fasting
The 5:2 and 16:8 approach are the most common types of intermittent fasting and differ in their daily approach.
5:2 Fasting Method: Two non-consecutive days out of the week are considered “fast days” in which only 25 percent of daily calorie needs are consumed . On the other five days, you eat at your normal calorie level. Some have taken this method one step further by doing a 4:3 approach where a “fast day” is alternated with a day of regular intake.
16:8 Fasting Method: All daily calories are eaten within an 8- to 10-hour window that you choose, but nothing is eaten the other 14 to 16 hours in the day. People often skip breakfast and choose an 8-hour eating window like 11 a.m. to 7 p.m.
Neurobiological Mechanisms Of Fasting
Studies have shown that changes in some neurotrophic factors and neurotransmitters caused by fasting may participate in fasting-induced emotional enhancement . Fasting can stimulate neurogenesis and enhance synaptic plasticity, which can regulate pain sensations and enhance cognitive function and the antiaging ability of the brain. These beneficial effects may be associated with changes in neurotrophic factors and neurotransmitters .
Serotonin release and turnover can increase during prolonged fasting . Increased output by the serotonergic system may cause an elevated mood and reduced pain sensitivity . Studies on rats have shown that the availability of brain tryptophan and serotonin increased during fasting, which may explain the effects of fasting treatments in migraineurs . In addition, brain-derived neurotrophic factors caused by intermittent fasting may be related to central serotonergic regulation . Furthermore, a research indicates that BDNF and serotonergic signaling have a reciprocal relationship, in which BDNF enhances the production and release of serotonin .
Another potential mechanism of mood enhancement is related to changes in the release of endogenous opioids caused by fasting. The plasma -endorphin levels of subjects who fasted for 5 to 10 days increased significantly during the fasting period .
Read Also: Can You Eat Anything On Intermittent Fasting
Physiology Of Fuel And Metabolism
Typically, our bodies are fuelled by glucose, which is a simple sugar. However, through diet restriction or intermittent fasting, that energy source gradually becomes unavailable.
As a result, the body begins to convert its stored fat into fatty acids that are easily absorbed by the bloodstream. Fatty acids produce molecules called ketones. After 8 12 hours of fasting, our metabolism shifts to replace glucose with ketones as our new source of energy.
Studies show that intermittent fasting may be better for you than other dietary strategies. This is because unlike glucose, ketones put less stress on our cells, they anti-inflammatory in nature and are a superior source of fuel for our bodies and brains.
How Do Calories Consumed Affect Metabolism
In general, if you significantly restrict calories, your metabolism will likely slow down to conserve energy. This is a survival mechanism and may kick in if you find yourself say, trapped on a deserted island with very little food. Your body will naturally slow down to help you survive.
It makes sense, then, that going on a dietin which you decrease the number of calories you consumemay also slow down your metabolism. Its a cruel trick of nature that when you cut back on calories to lose weight, your body adapts by slowing your metabolism down.
The bad news is that when you go back to eating your regular diet, the body often fails to pick back up again. Instead, it maintains that slower metabolism even though youre eating more. Thats why you can suddenly regain the weight you lost and often even more.
Several studies have found this to be true, particularly during significant calorie restriction. In a 2006 study, for example, participants reduced their calories for four days. Results showed that they all experienced significant decreases in body weight, but also decreases in their BMR. The fewer calories they ate, the greater the decreases in their BMRs.
The conclusion seems to be that the less energy you take in, the less energy your body produces to match. Calorie-restrictive diets slow metabolism, and when the dieter goes back to consuming a normal amount of calories, the sluggish metabolism is unable to burn the extra energy, and the weight piles back on.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Normal Range For Fasting Blood Sugar
Eating Frequently Boosts Your Metabolism
Many people believe that eating more meals increases your metabolic rate, causing your body to burn more calories overall.
Your body indeed expends some calories digesting meals. This is termed the thermic effect of food .
On average, TEF uses around 10% of your total calorie intake.
However, what matters is the total number of calories you consume not how many meals you eat.
Eating six 500-calorie meals has the same effect as eating three 1,000-calorie meals. Given an average TEF of 10%, youll burn 300 calories in both cases.
Numerous studies demonstrate that increasing or decreasing meal frequency does not affect total calories burned (
9 ).
One study that compared eating three or six high-protein meals per day found that eating three meals reduced hunger more effectively .
That said, responses may depend on the individual. If frequent eating reduces your cravings, its probably a good idea. Still, theres no evidence that snacking or eating more often reduces hunger for everyone.
SUMMARY Theres no consistent evidence that eating more often reduces overall hunger or calorie intake. Rather, some studies show that smaller, more frequent meals increase hunger.
Fasting Puts Your Body In Starvation Mode
One common argument against intermittent fasting is that it puts your body into starvation mode, thus shutting down your metabolism and preventing you from burning fat.
While its true that long-term weight loss can reduce the number of calories you burn over time, this happens no matter what weight loss method you use .
Theres no evidence that intermittent fasting causes a greater reduction in calories burned than other weight loss strategies.
In fact, short-term fasts may increase your metabolic rate.
This is due to a drastic increase in blood levels of norepinephrine, which stimulates your metabolism and instructs your fat cells to break down body fat (
29 ).
One study showed that fasting every other day for 22 days did not lead to a reduction in metabolic rate but a 4% loss of fat mass, on average .
SUMMARY Short-term fasting does not put your body into starvation mode. Instead, your metabolism increases during fasts of up to 48 hours.
Read Also: Is Fasting Necessary For Psa Test
You Will Be Hungry All The Time
Many feel that eating one meal a day will only lead to a constant feeling of hunger.
When there is a change in the system, this will be normal. Especially in the beginning of fasting such as eating one meal a day. The type of food you are eating can also cause a feeling of hunger.
Eating foods high in fiber can help you feel fuller for longer periods of time.
This sense of hunger can also be in the mind. I used to look at the time and feel I had to eat because it was just that time.
Many will also feel hungry, but its only because they are thirsty. This sense can also lead to overeating when its time for your meal.
How To Keep Metabolism High While Fasting
While some metabolism downregulation is expected due to weight loss, not so much intermittent fasting, there are things we have within our power to change.
There are a multitude of reasons why you may not be losing weight or hit a plateau. Want to find out more? Check out my article on the 11 Reasons Why You’re Not Losing Weight On Keto.
Don’t Miss: How To Track Intermittent Fasting
Does Intermittent Fasting Make Your Metabolism Slow Down
Rick KaseljFeatured, Food, Health, Healthy Living
If you want to lose weight, youve probably considered fasting. Currently, intermittent fasting is the most popular type, and involves cycling between periods of eating and periods of fasting. This method, studies have found, can not only help you lose weight but may have other health benefits as well.
On the other hand, you may have heard that if you go on any type of fasting diet, it may cause your metabolism to slow down, which could make you even more prone to weight gain in the future.
Is this true, and if so, should you skip this weight-loss method?
Fasting Slows Down Your Metabolism Is It A Myth
Fasting has always been believed to be equivalent to starvation. People often equate fasting to a lack of food in the body, and any lack of food in the body reduces the bodys metabolic rate. If you do not give your body enough food for longer durations, it will surely start to slow down its metabolic rate and start operating at a lower power.
However, once the everyday foods are introduced into the body, this metabolic rate will stay the same, and you will end up gaining weight. So, if we equate fasting with starvation or eating calories 15-50% less than the body requires, the metabolic rate goes down.
But, intermittent fasting is different. In this, you eat healthy foods and follow an eating and fasting pattern. So, you are not starving your body, and hence it will not activate the defence response and starvation mode.
So, does fasting slow your metabolism? No, intermittent fasting does not slow down metabolism however, starvation and eating fewer calories than your daily requirement does. On the other hand, intermittent fasting either increases the metabolic rate or keeps it stable.
Also Check: How Does The Fasting Mimicking Diet Work
Use Whole Grains Instead Of Flour
Whole grains are harder to digest thus, your body uses up more calories. This strategy can help you reduce calorie intake while digesting the food. Additionally, whole grains tend to be only a little processed. So they are richer in terms of nutrition as compared to flour or milled grains.
Whole grains are also rich in fiber and will promote better digestion, thus improving your gut health as well. We recommend starting your breakfast with whole grains like oatmeal or barley. Furthermore, you can substitute white rice with brown rice and white bread with grain bread.
Why Might Changing Timing Help

But why does simply changing the timing of our meals to allow for fasting make a difference in our body? An in-depth review of the science of IF recently published in New England Journal of Medicine sheds some light. Fasting is evolutionarily embedded within our physiology, triggering several essential cellular functions. Flipping the switch from a fed to fasting state does more than help us burn calories and lose weight. The researchers combed through dozens of animal and human studies to explain how simple fasting improves metabolism, lowers blood sugar levels lessens inflammation, which improves a range of health issues from arthritic pain to asthma and even helps clear out toxins and damaged cells, which lowers risk for cancer and enhances brain function.
Don’t Miss: How To Lose Weight Doing Intermittent Fasting
Top Off Your Water Tank
“Your body is 80% water if you don’t drink enough, your cortisol levels will be raised, which will keep you from being able to reduce tummy fat,” says doctor of chiropractic Susan Wong, DC, co-founder of Twin Waves Wellness Center. Wong recommends women consume 2 to 3 liters per day, and 3 to 4 liters daily for men.
May Increase Your Life Span
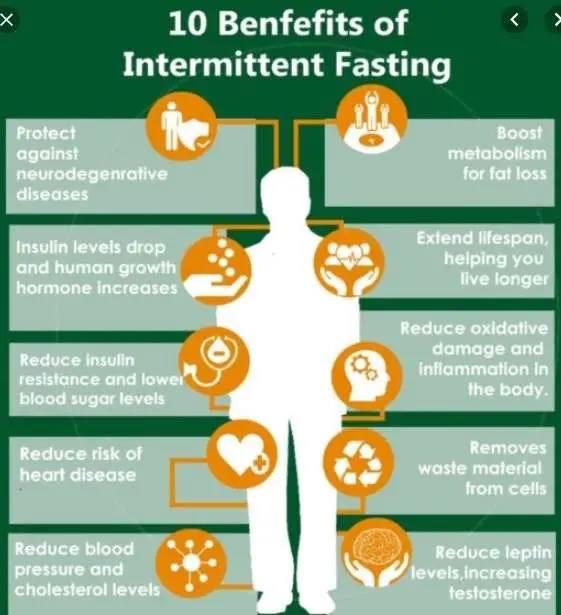
There are several reasons that intermittent fasting may positively impact our life span weight loss, decreased blood pressure, and most of the benefits we listed above may all contribute to prolonging our life while also increase our quality of life at the same time.
Intermittent fasting has been found to affect longevity in animal studies, having beneficial effects on life span and markets for health, stress, metabolic response, and age-related diseases .
These findings are hard to confirm in human trials as there are many factors that affect epidemiological studies and many different types of fasting. But at the end of the day, some of the benefits of intermittent fasting may increase our quality of life overall and reduce our risk of developing chronic diseases.
Read Also: Is Intermittent Fasting Good For High Blood Pressure
Try To Cut Down The Stress
All the stressors of life can directly contribute to your weight. Most of the time, the first thing that you do when youre stressed is to eat more. Moreover, the food we turn to is junk food or food high in sugar content.
When you are stressed, your body releases cortisol. Usually, cortisol prepares your body for emergency response or the fight-or-flight response. It goes down when the stressful stimuli are gone.
Cortisol can become harmful over long periods because it stimulates your appetite. Thus, you eat more. However, stress also affects your ability to metabolize the increased amount of food. The worst part is that all the fat you gain from overeating will be deposited as belly fat.
We recommend adopting strategies to help manage your stress levels. This can include meditation, music therapy, exercising, getting a new hobby, and more. Stress doesnt just slow your metabolism, but it also puts you at risk for other diseases like high blood pressure.
Does A Slow Metabolism Put Me At Risk For Things Other Than Weight Gain
A slow metabolism can cause you to have lower energy levels. Since your body is taking so long to break down the food, you have lesser energy available to you. The lower energy levels can cause you to feel fatigued.
Other than that, the weight associated with a slow metabolism can put you at risk for other diseases associated with obesity. Obese individuals are more likely to have heart issues, hypertension, insulin resistance, diabetes, and other such diseases.
You May Like: How Many Calories Should You Eat When Doing Intermittent Fasting
Up Your Caffeine Intake
Caffeine can help your body use more of its fatty energy reserves. The more your caffeine intake, the more your body will release noradrenaline. This hormone promotes fat breakdown, which can boost your metabolic rate.
However, you can become tolerant of caffeine. Thus, we recommend drinking coffee with breaks. This will keep your body from building a tolerance toward it and allow you to reap the benefits for a longer time.
It May Lead To Improvement In Many Health Conditions
A 2020 study funded by the National Institutes of Health and published in the New England Journal of Medicine analyzed decades of previous research and found that intermittent fasting can lead to improvements in health conditions, including obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, cancers and neurological disordersResearch on intermittent fasting shows health benefits. National Institutes of Health. Accessed 6/21/2021. .
Also Check: What Can You Eat Intermittent Fasting
Should I Never Eat Burgers And Other High
As such, there is no food that you should absolutely avoid. However, you should consume everything in moderation, especially fast food. You can set a routine that allows you to eat the foods you like once or twice a week.
You can also try to make the meals you like with healthier ingredients. Use less oil in your food or use an airfryer. Try to change the buns you use. Switch your cereal to something a little less processed and use whole grains instead of polished ones. These small changes will help you age more slowly and stay in shape for longer.
Glucose And Its Working Principle
Brain activity almost entirely relies on glucose as energy . Glucose in the blood is metabolized in brain areas that need to perform specific tasks . Glucose provides the energy for neurons to fire impulses to support cerebral function. Therefore, the brain needs adequate glucose to function effectively . When blood glucose levels are severely low, brain function will be severely disturbed, resulting in a large number of cognitive and behavioral deficits, such as impaired coordination, blurred vision, amnesia, weird behaviors and personality changes, confusion, and anxiety. Relatively subtle changes in glucose can also have an important impact on thinking and behavior .
Read Also: How Much Time For Intermittent Fasting
What Fasting Does To Metabolism
When you severely limit calories, your body senses this shortage of fuel and slows down its functioning to conserve energy. Instead of boosting your metabolism, you may experience a suppression of your resting metabolism equal to as much as 20 percent. Your resting metabolism is based on the energy your body uses to fuel basic functions, such as pumping blood and breathing. These activities don’t stop, your body just becomes more efficient and burns fewer calories to do them than it would when adequately fed.
This is one of the reasons very low-calorie diets and fasts don’t often bring about the results you’d expect. Your body is fighting what it perceives as starvation by slowing the rate at which it burns calories.
