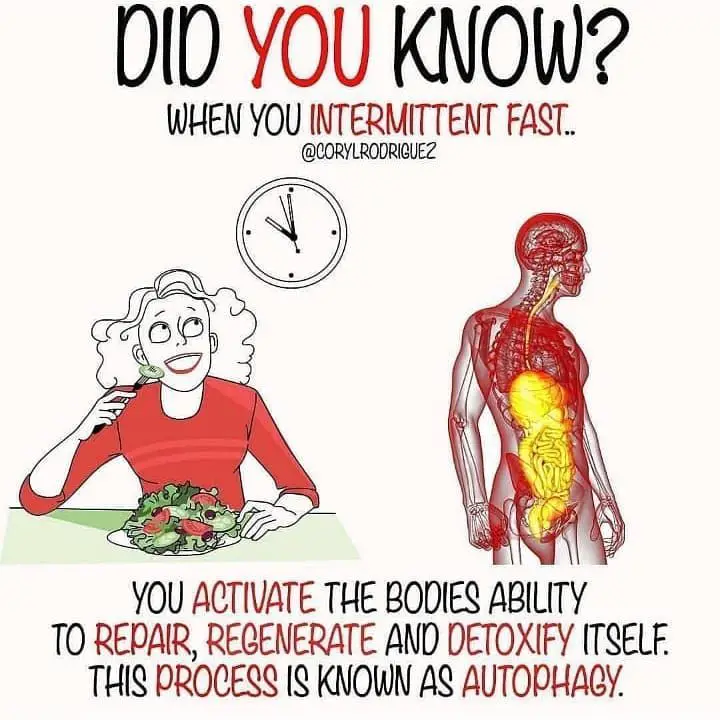
Is Intermittent Fasting Truly For Everyone
5 min read.Shrabonti Bagchi
The fasting method not just helps in losing weight, but can improve the gut microbiome, insulin efficiency and mental acuity. But can everyone do it?
For probably the first time in the history of diets from the vinegar and biscuits bamming of the Regency era to the modern paleo and keto diets one diet type has got an overwhelmingly positive nod from nutritionists and doctors. They may disagree on the finer points of how one practises it, but experts across the panel largely agree that periodic fasting is good for the human mind and body, and positively impacts a large number of functions, from enhancing the diversity and health of the gut microbiome to increasing insulin efficiency in the body and kickstarting a sluggish metabolism.
India likely to receive EU’s Euro 300 billion fund unde …
Studies have shown that intermittent fasting can change the makeup of the gut microbiome, encouraging the growth of good bacteria like Akkermansia muciniphila associated with decreased intestinal inflammation and a healthier gut. Other studies on animal subjects have shown a link between IF and reduction of brain inflammation, ultimately slowing down the neuro-degenerative process that causes diseases like Alzheimers in humans.
Heavy rain, landslides likely in north Bengal over next …
It Boosts Microbiome Diversity
We already mentioned a study on IF that revealed an increase in Akkermansia. Turns out that there is more.
In a recent study performed on patients suffering from multiple sclerosis, an increased abundance of the following microbial families was observed after 4 weeks of IF11:
- Faecalibacterium
Among these, it is important to highlight the importance of Lactobacillus, which is a well-known probiotic strain that has been recognised for its multiple benefits on gut health.
Another appealing finding in this study was the enrichment in Faecalibacterium, which is usually present in reduced levels in individuals who suffer from gastrointestinal inflammatory diseases such as Inflammatory Bowel Disease . This microbe is linked with inflammatory properties and it has even been suggested to contribute to a marker of healthy-gut12.
Intermittent Fasting Is Not A Magic Fix
As great as Intermittent Fasting is, it is always important to remember that it is not a magic fix for all your health and fitness problems.
If you suffer from specific gut problems, work with a doctor or someone who specializes in gut health to heal your gut. Intermittent Fasting will complement and enhance those gut-healing efforts, and once youve healed, will help you better maintain that happy gut.
Recommended Reading: What To Eat While Fasting
May Help Prevent Cancer
Cancer is characterized by uncontrolled growth of cells.
Fasting has been shown to have several beneficial effects on metabolism that may lead to reduced risk of cancer.
Promising evidence from animal studies indicates that intermittent fasting or diets that mimic fasting may help prevent cancer. Research in humans has led to similar findings, although more studies are needed (
However, more research in humans is needed.
SUMMARY
Studies in animals suggest that intermittent fasting may be protective against neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimers disease.
Nutrition And Fasting Interventions For Mitochondrial Health
Specific nutrients that support mitochondrial function may be part of a personalized nutrition strategy for some patients. In other cases, a form of intermittent fasting may be appropriate and blended with a food plan to create an individualized nutrition intervention. Several forms of intermittent fasting* include the following:
- Alternate-day fasting: A cycle of fasting on one day and eating on the next day.
- Time-restricted feeding: An approach that considers circadian rhythms and advocates consuming calories from food and beverages only during a shortened window of time daily, also called prolonged nightly fasting, which extends a persons nightly fast to 12 hours or more.
- Fasting-mimicking diet: A periodic, multiple-day, plant-based diet program low in calories, sugars, and protein but high in unsaturated fats with the inclusion of supplements for vitamins, minerals, and essential fatty acids.
All can be effective, but in my work with patients, I have found that time-restricted eating is the most practical and sustainable approach for most people.There is some evidence that eating only in the morning or daytime is better than later in the day and evening.
If you would like to give time-restricted eating a try, make sure to start slowly to give your body a chance to adapt.
You May Like: What Is 5 2 Fasting
Putting The Benefits Of Intermittent Fasting For Gut Health All Together
Health is more than a weight scale. With fasting, weight management is just one of the MANY benefits.
My favorite ROI from intermittent fasting is knowing that Im charging my mitochondria day-in and day-out. Our mitochondria are the energy-producers of the body arguably, mitochondrial health in the number ONE factor for healthy aging.
With intermittent fasting, I process food much more efficiently and promote less cellular aging as a result. Long-term, it helps to know that intermittent fasting is associated with less risks for autoimmunity, inflammation, cancer, mood disorders, cognitive decline, hypertension, & cardiovascular disease too.
Try it and see the results for yourself.
Does Intermittent Fasting Benefit Gut Health
Intermittent fasting or restricting your eating to certain hours of the day is popular for a variety of reasons including aiding weight loss and better blood sugar and insulin control. Some say intermittent fasting can also help people age better, live longer and reduce inflammation, though the research on these benefits is far from conclusive.
Another buzzy potential pro of intermittent fasting: better gut health. But, like many of the proposed effects of intermittent fasting, research on the topic is scant. So, if youre interested in a healthier microbiome and wondering if its worth trying intermittent fasting, heres what experts have to say:
Read Also: What Verses To Read When Fasting
Fasting Vs Counting Calories
Fasting is a way to get the benefits of Ketosis without needing to be hyper-vigilant about counting calories. You can determine your own program by finding a cycle that works best for you, and then focus your energies on following a healthy diet during your eating hours.
The Gut health benefits of incorporating fasting into your lifestyle are remarkable! And, in addition, you may discover that fasting also improves your energy, digestion, sleep, and mood but it also is surprisingly easy to add to your lifestyle!
Fasting has been practiced for millennia, but only recently studies have shed light on its role in adaptive cellular responses that reduce oxidative damage and inflammation, optimize energy metabolism, and bolster cellular protection.
… Regular fasting extends longevity in part by reprogramming metabolic and stress resistance pathways.
In rodents, intermittent or periodic fasting protects against diabetes, cancers, heart disease, and neurodegeneration, while in humans it helps reduce obesity, hypertension, asthma, and rheumatoid arthritis.
This research indicates that fasting has the potential to delay aging and help prevent and treat diseases while minimizing the side effects caused by chronic dietary interventions.
US Library of Medicine Abstract. Fasting: Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Applications, V. Longo and M. Mattson
Additional Benefits Of Intermittent Fasting
Aside from its possible benefits for our gut, intermittent fasting has been long studied for other potential health benefits, including aiding in weight loss, improving insulin resistance, reducing inflammation, and improving blood pressure. These effects can help reduce the risk of developing other chronic conditions such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and even cancer.
Many people who decide to do IF are doing it for its potential benefits for weight loss. A big factor in helping with losing weight is time-restricted eating during IF. The less time you can eat, the fewer calories you will likely intake if you dont over-consume during your eating period. Some studies also suggest that short-term fasting helps to increase your overall metabolism so that you can lose weight faster.
IF has also been touted for its ability to help protect against type 2 diabetes by improving insulin resistance. This is done by helping to decrease overall body weight as well as reducing blood sugar levels. Other studies have found IF to show promise in helping to reduce inflammation in the body, another risk for chronic diseases, including type 2 diabetes. In addition, some studies have shown IF to help improve our resistance to oxidative stress.
Additional Benefits of Intermittent Fasting
- Improved blood pressure
Read Also: How To Start The Intermittent Fasting
Fasting Improves Gut Bacteria
Its true. Fasting can improve certain species of bacteria that are associated with health outcomes. This has been a consistent finding in studies looking at the impact of fasting on the microbiome.
In fact, just recently intermittent fasting was put to the test in a clinical trial. The researchers wanted to see if intermittent fasting would influence the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut. It turns out they were right. They found two species were significantly increased: Akkermansia mucinophila and Bacteroides fragiles. That may not mean much to you but these two species are known to have significant health-promoting effects. Akkermansia for example, helps maintain the health of the intestinal barrier.
Thats not all.
Something called the Firmicutes:Bacteroides ratio, a well known microbiome marker for overall health is improved with intermittent fasting. Obesity and metabolic syndrome are associated with less favorable ratios.
Investigators have also determined that some of the health benefits of fasting, like improving fatty liver and obesity are attributed directly to gut bacteria. As it turns out, those health benefits are wiped out when mice fast in the absence of any gut bacteria!
Clearly we are just scratching the surface on this topic however, in many chronic disease states if you improve the microbiome, you improve the health of the person.
But
Before we all rush to the fasting table, lets have a discussion on what to watch out for.
Intermittent Fastingregimen To Improve Gut Health
Some of the more well-researched intermittent fasting regimens include the 16:8 method, where you fast for 16 hours and can eat within 8 hours of your choosing, such as 12-8 pm, and the 5:2 method, where you eat normally 5 days out of the week and then limit your caloric intake to < 600 the remaining calories 2 days out of the week, or a full 24 hour fast 1-2 times per week.
The specific intermittent fasting regimen you choose will vary from person to person. Some may find they do best with a 16:8 regimen, while others may prefer a full 24-hour fast 1-2 days a week. When choosing your intermittent fasting method, be sure to choose one that feels sustainable for you and allows you to incorporate a healthy diet that includes a variety of different whole foods to maximize its benefits. Additionally, apps like DoFasting, can help keep you on track and informed when it comes to your IF routine.
Before starting an intermittent fasting regimen, consider your overall diet. Research on intermittent fasting and its benefits regarding gut health still requires more research, whereas there is a lot of research regarding diet and its effect on our gut. To get the most out of your IF routine for a healthy gut, be sure to include a variety of whole foods in your diet and emphasize probiotic and prebiotic food sources, such as fermented foods and fiber-rich fruits and vegetables.
Article Contents
You May Like: What Can I Have While Intermittent Fasting
How To Build A Complete Gut Health Routine With Intermittent Fasting
Main image courtesy of Daily Nebraskan.
Trying to be and stay healthy is and should always be a main priority in your life. There are so many factors that you have to consider in order to continue to stay healthy, such as focusing on your brain health, colon health, skin health, hair health, gut health, and much more. While it sounds difficult, there are actually many lifestyle changes that you can make in order to change your life for the better.
One of the most essential parts of your body to keep healthy is your gut health because of just how your gut health plays an important part of your overall health. Feeding your gut the best types of foods, supplements, and more is among some of the best ways that you can achieve near-perfect gut health.
Have you ever heard of intermittent fasting? It can actually provide a lot of amazing benefits to your body, especially your gut health, so why not learn more about it?
Continue reading to learn:
- How Can Intermittent Fasting Affect Your Gut Health?
- Intermittent Fasting: The Ultimate How-To
In Simple Terms: Why Does Intermittent Fasting Have So Many Benefits

Being in a fasted state activates cellular pathways that remove or repair damaged molecules and improve our defense against oxidative and metabolic stress.Evidence now indicates that intermittent fasting has several positive effects that are unrelated to weight, including:
- Improving blood sugar regulation, heart rate, and blood pressure
- Increasing stress resistance
- Slowing the effects of aging
- Reducing inflammation
- Improving cognitive function
Also Check: How Effective Is Fasting For Weight Loss
How Fasting Changes Your Gut Microbiome
The timing of eating matters.
Little living things deep in our bowels hold a mysterious grasp on the balance within our bodies. One change to our food regimen what we eat, how much of it, and when and the biological harmony can be thrown off.
This we know. What dont know is exactly how the tiny microbes that make up the gut microbiome harness their power. This knowledge is necessary for truly understanding what fasting does to the gut microbiome.
But in the meantime, animal studies on intermittent fastings effects on the gut microbiome do suggest the eating pattern could eventually be used for good potentially as a treatment for diabetes, a way to boost immunity, and a way to transform bad fat to good fat.
What you should know first While these studies are promising, theres a caveat: Theyre mostly from mice. These ideas arent validated by human studies, also known as clinical trials.
If you look at it closely, there’s clearly a deficiency in many areas of this microbiome field, a deficiency of well-controlled, randomized controlled studies in humans, Dr. Emeran Mayer tells Inverse.
Mayer co-authored a 2021 review published in the journal Nutrients on the relationship between intermittent fasting and gut health as it relates to weight loss. Hes a professor at the David Geffen School of Medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles and runs the UCLA Brain Gut Microbiome Center.
If Preserves Gut Homeostasis And Is Associated With Reduced Bacterial Abundance
Maintenance of gut homeostasis has been shown to play an important function in the determination of lifespan in Drosophila . Midgut tissue homeostasis is maintained by intestinal stem cells , which are arranged along the basement membrane and respond to stress and lead to a regenerative response. In the aging female fly gut, ISC proliferation becomes dysregulated and can lead to mis-differentiation and hyperplasia in the intestine. DR reduces gut pathology in aging females , and we therefore sought to examine the effects of IF on gut homeostasis.
Early-Life Fasting Leads to Long-Lasting Improvements in Gut Health and Reduced Bacterial Load
ISC activity. Representative confocal fluorescence z projections of midgut regions 4/5 from 70-day-old ad libitum, 5-day IF, and IF switch flies stained with DAPI and anti-phospho-H3 antibody are shown. The scale bar represents 100 m.
Quantification of pH3-positive cells per gut. After 5 days of fasting, 70-day-old 5-day IF guts had significantly fewer pH3+ cells compared to ad libitum controls . IF switch guts, after 40 days on food, also had significantly fewer pH3+ cells compared to ad libitum controls . 19 or 20 guts per condition are shown. Data are shown as mean ± SEM.
Barrier function at day 60, as measured by smurf flies with leaky intestines, was significantly improved in IF switch females compared to ad libitum controls .
Read Also: How Much Weight Loss With Fasting
Intermittent Fasting And Working Out Fight Against Obesity
Many types of research establish a strong connection between obesity and gut health. For example, certain amino acids might influence both the microbiome and obesity. Particular types of food such as processed foods and artificial sugars can change the diversity of the flora, as well as the metabolites these microorganisms create. Microbes, viruses, and even fungi have long been one of the primary factors that affect a persons metabolism. 2017 research in Cell Metabolism revealed intermittent fasting, especially an every-other-day fast, can promote brown fat.
It means this fatty tissue has more mitochondria to produce more heat or energy. In the process, brown fat can burn a significant amount of calories. It does this on the gut level. As mentioned, intermittent fasting and working out can change the activity and diversity of the microbiome. One of these changes can be the increased production of fermented products known as acetate and lactate, which then leads to activities that enhance the browning of the fatty tissues. These fermented products can further improve metabolism by promoting better insulin action, especially among morbidly obese individuals. By decreasing the risk of insulin resistance, the odds of developing diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease also goes down.
What is insulin resistance? It is a condition wherein cells become less accepting of insulin, a hormone that delivers glucose or blood sugar.
Your Digestive System Needs Time To Reset
Your digestive system is like another world that exists in your body. This microbiome has its own rhythm, too, and it behaves differently depending on what you are doing, according to MindBodyGreen. This cycle resets itself every day, and eating several times throughout the day might disrupt this rhythm. Disturbances can lead to an imbalance in gut bacteria, which might raise the risk of some health issues, including insulin sensitivity or obesity.
Fasting gives your gut microbiome a chance to return to normal, and the good news is you don’t have to fast for a long period of time to see results. MindBodyGreen notes that positive changes can begin in just a few hours, and your body might experience even greater changes after only a few days of fasting. Fasting isn’t for everyone, however. If you have any health issues that could be affected by fasting, check with your doctor before starting a plan.
Also Check: Does Fasting Help With Arthritis
